Fig. 3.
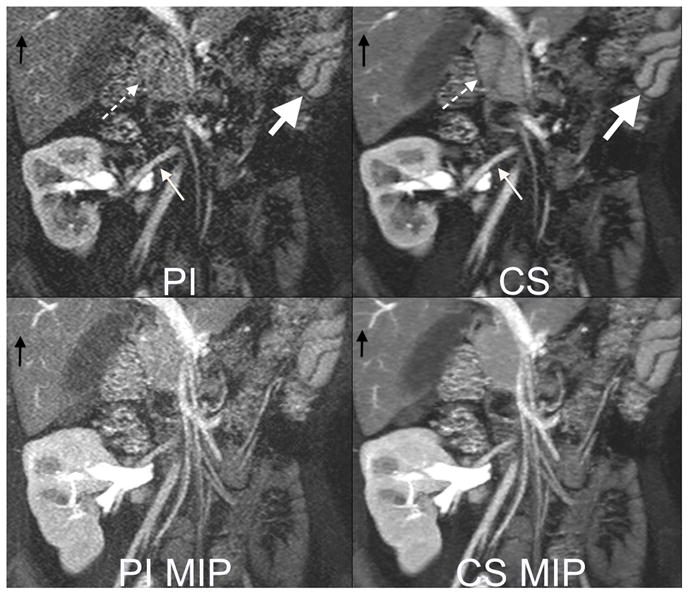
6 year old female with a transplanted kidney. Top: Cropped images from a 13 second 3 Tesla acquisition with 32 channels and an acceleration factor of 6. The high acceleration factor permits 320x320 matrix with 2 mm slice thickness. Note improved delineation of artery to the kidney (small white arrow), head of the pancreas (dashed arrow), small vessels in the liver (black arrow) with compressed sensing (CS) reconstruction than parallel imaging (PI) reconstruction. The fast acquisition also permits capturing fast perfusion dynamics, as seen by the differences in contrast enhancement of the splenic red and white pulp tissues (big white arrow). Bottom: Maximum intensity projections (MIP) highlight improved image quality with decreased noise afforded by the CS reconstruction.
