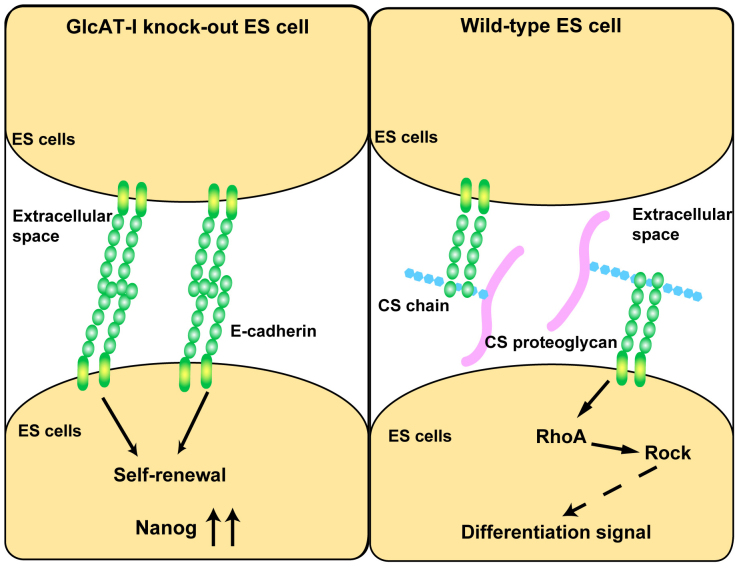
Figure 7. CS controls the functional integrity of ESCs by binding to E-cadherin.
In GlcAT-I−/− ESCs, homophilically interacting E-cadherin inhibits the differentiation of ESCs due to the disruption of the binding of CS to E-cadherin. On the other hand, in Wt ESCs, the interaction between CS and E-cadherin stimulates the tendency of ESCs to differentiate by counterbalancing signaling pathways and transcription factors that promote native pluripotency.