Figure 4. Transgenic validation of cis-regulatory modules associated with nephrogenic determinants that are co-bound by Six2 and β-catenin.
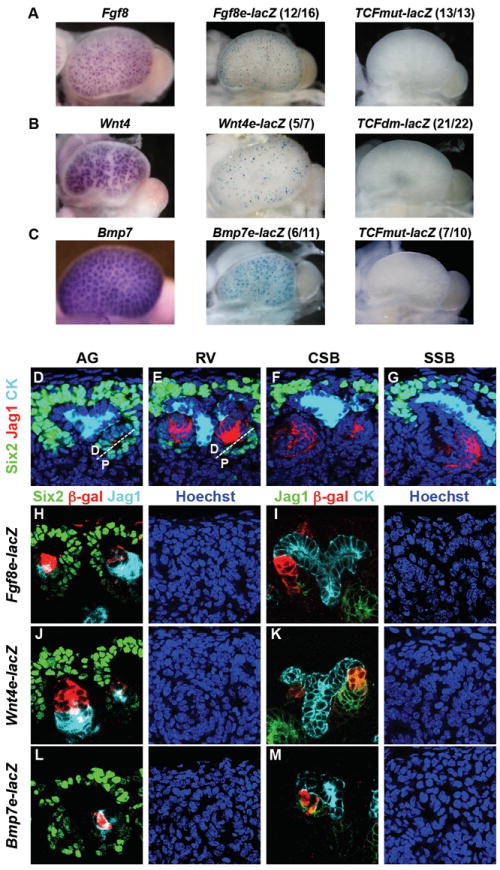
(A-C) Whole mount in situ hybridization detects expression of endogenous genes (left panels). β-galactosidase activity of transgenic reporter driven by the putative CRMs identified through Six2 and β-catenin co-binding (middle panels). β-galactosidase activity driven by the CRMs with mutated Lef/Tcf binding sites (right panels). The ratio indicates the number of embryos showing the illustrated expression pattern over the total number of transgenic progeny, each from a unique founder. (D-G) Expression of Six2 and Jag1 in the pretubular aggregate (AG), renal vesicle (RV), comma-shaped body (CSB), and S-shaped body (SSB) stages of nephrogenesis in the mammalian kidney. The AG and RV are shown divided into the distal and proximal parts by a white dashed line. Jag1 is expressed in the lumen of AG, at the distal part of RV, and at the medial segment of SSB. Six2 is expressed in undifferentiated nephron progenitors and downregulated in AG and RV. Cytokeratin (CK) marks the ureteric epithelium. (H-M) Expression of reporters driven by CRMs co-bound by Six2 and β-catenin in E15.5 transgenic kidneys.
