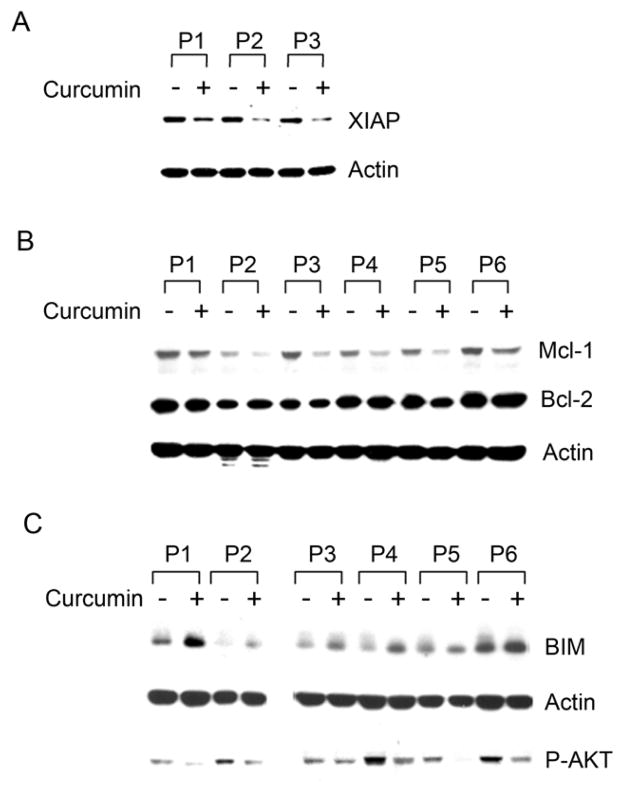
Fig. 3. Curcumin modulates the expression of certain pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins in CLL B-cells.
Lysates of CLL B-cells isolated from various patients as indicated treated with curcumin were analyzed to assess the effect of curcumin on the anti-apoptotic proteins XIAP (n=3), Mcl-1 (n=6), and Bcl-2 (n=6) as well as the pro-apoptotic protein BIM (n=6) using specific antibodies. Actin was used as the loading control. Curcumin treatment of CLL B-cells suppressed the expression of XIAP (A) and Mcl-1 (B, top row) but, not Bcl-2 (B, middle row). Curcumin treatment of CLL B-cells also resulted in up-regulation of the pro-apoptotic protein BIM expression (C, top row). AKT is the upstream negative regulator of BIM expression. Inhibition of AKT-phosphorylation by curcumin (C, bottom row) is also shown.