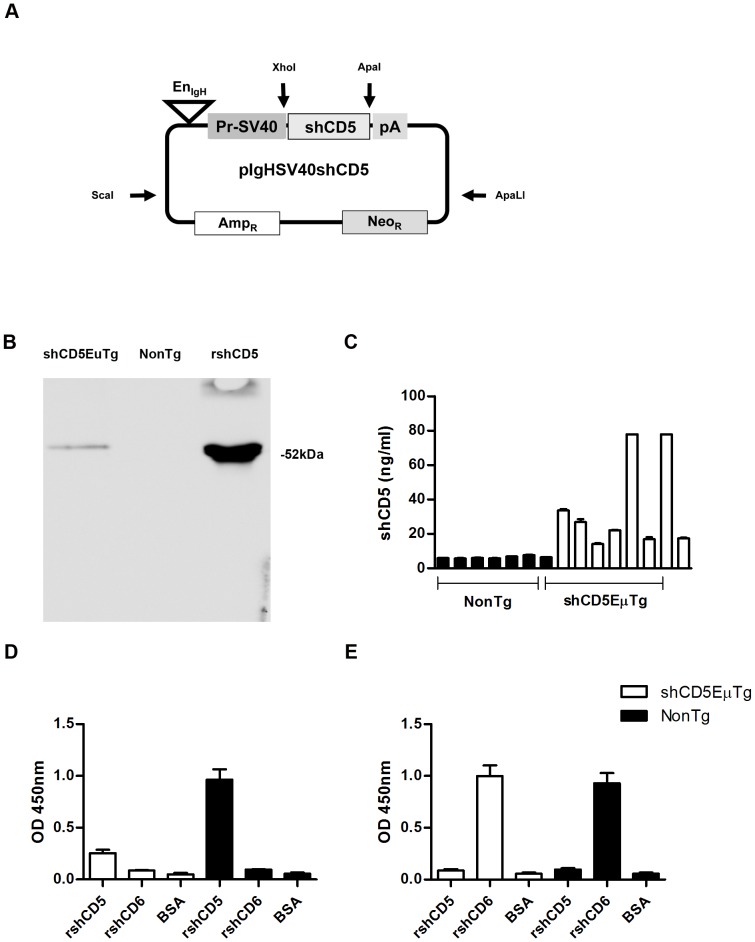
Figure 1. Generation and characterization of human soluble hCD5 transgenic mice (shCD5EμTg).
A) Structure of the pIgHSV40shCD5 targeting vector. The cDNA sequence for shCD5 was inserted as XhoI-ApaI in between the promoter and polyA sequence of the pIg vector and then isolated as ScaI-ApaLI fragment for oocyte injections. B) Western blot analysis of human CD5 immunoprecipitates from transgenic (shCD5EμTg) and non-transgenic mice (NonTg) sera. The anti-CD5 Cris-1 mAb coupled with CNBr-activated Sepharose beads was used as immunoprecipitating agent. Western blotting was then carried out using the Leu-1 mAb plus HRP-labeled anti-mouse Ig. As a positive control, purified rshCD5 (50 ng) was included. C) ELISA detection of shCD5 in sera from shCD5EμTg mice. Sera from transgenic (shCD5EμTg, white) and non-transgenic littermates (NonTg, black) mice were analyzed by sandwich ELISA using Cris-1 and biotin-labeled Leu-1 as capture and developing mAbs, respectively. A standard rshCD5 curve was also analyzed in parallel to quantify results. D–E) shCD5EμTg mice are tolerant to exogenously administered rshCD5 but not rshCD6. shCD5EμTg mice and wild-type littermates were immunized twice with rshCD5 (D) or rshCD6 (E) (25 µg) in Freund's adjuvant (complete and incomplete, sequentially) within a 3-week interval. Mouse sera were collected 2 weeks after the boosting and added to ELISA plates coated with purified rshCD5, rshCD6 or BSA, then developed with a HRP-labeled anti-mouse IgG. Values represent the mean OD 450 nm values ± SD obtained in triplicate determinations for each sample (five mice per group). The total concentration of IgG was similar for both groups.