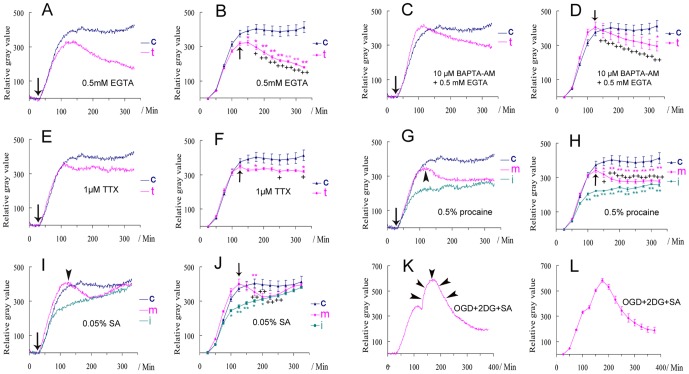
Figure 3. The effects of different treatments on the biophotonic activities in mouse coronal brain slices.
(A–D) Removing extracellular Ca2+ (A and B, 0.5 mM EGTA, n = 6) or removing intra- and extracellular Ca2+ together (C and D, 10 µM BAPTA-AM+0.5 mM EGTA, n = 6) from the beginning of the application of 50 mM glutamate (pink line in A and C). The changes were significant during the maintenance period (B and D). (E, F) 1 µM TTX had no influence on the initiation, but partly on the maintenance (pink line, n = 5). (G, H) Both initiation (green line, n = 5) and maintenance (pink line, n = 6) were significantly affected by 0.5% procaine. (I, J) Both initiation (green line, n = 6) and maintenance (pink line, n = 6) were significantly affected by 0.05% sodium azide (SA), but a recovery was found after long-lasting application. Arrows indicate the treatment at the beginning of the application of 50 mM glutamate in A, C, E, G and I and arrowheads mark the treatment that began after the achievement of the maximum effect in G and I. t: treated group; c: control group (blue line) is same in A–J (n = 6), i: the treatment together with application of glutamate (initiating period), m: the treatment during the maintenance period. Data show mean±s.e.m. n = the number of slices from the same number of mice. * treated group (corresponding color) versus control at the same time periods; + the maximum effect just before treatment versus the effects after (arrows in B, D, F, J) in treated group. * or + P<0.05, ** or ++ P<0.01. (K, L) Oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD, 95% N+5% CO2), together with the application of 5 mM 2-deoxy-D-glucose (2DG) and 0.05% SA during the maintenance period, tended to significantly inhibit the biophotonic activities in a gradual way (n = 6), but the effect of slice washing still existed and even lasted for a relatively long time (increasing part, arrowheads).