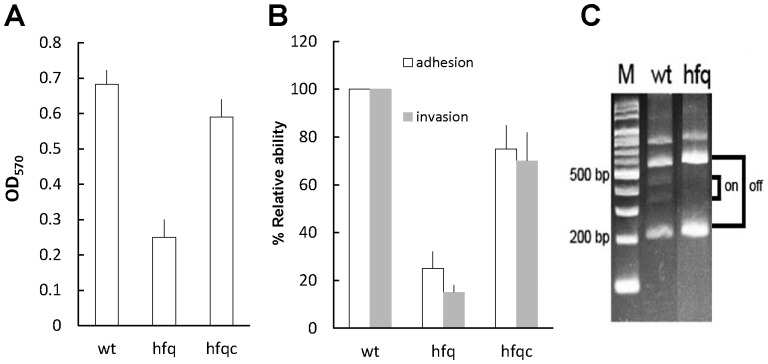
Figure 5. P. mirabilis hfq was required for biofilm formation, adhesion and invasion of uroepithelial cells and expression of MR/P fimbriae.
(A) Biofilm formation in wild-type, hfq mutant and the Hfq-complemented strain. The biofilm level of the wild-type, hfq mutant and the Hfq-complemented strain was determined as described in Materials and Methods. The optical density (OD570) of the solution extracted with 95% ethanol correlated with the level of biofilm formation. (B) Adhesion and invasion abilities of wild-type, hfq mutant and the Hfq-complemented strain. Abilities to adhere to and invade NTUB1 cells were determined by assays as described in Materials and Methods. The adhesion or invasion ability of wild-type was set at 100% and other data were relative to this value. (C) The promoter direction of mrp operon in wild-type and hfq mutant by the invertible element assay. The assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods using overnight cultures. The “on” means direction of mrp promoter is for mrp operon expression. The data represent the average of three independent experiments with standard deviation in A and B. The representative result from three independent experiments is shown in C. wt, wild-type; hfq, hfq mutant; hfqc, Hfq-complemented strain; M, marker.