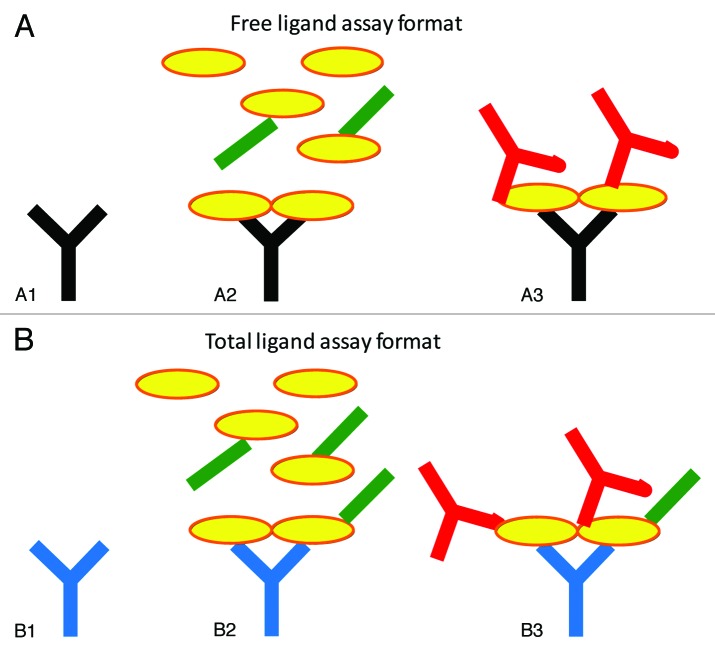
Figure 1. Schematic representations of the free (A) and total (B) ligand assays used in this study. The coating antibody (A1, black) in the free ligand assay binds to the same epitope as the therapeutic Fab. Thus, when samples containing ligand (yellow) and Fab (green) are added (A2), only free ligand should bind to the capture antibody, as long as there is no shifting of the equilibrium during analysis. The secondary antibody (A3, red) is a biotinylated anti-ligand antibody to allow detection. The total ligand assay (B) employs a capture antibody (B1, blue) that can bind the ligand in the presence of the anti-ligand Fab. When samples containing ligand (yellow) and Fab (green) are added (B2), both free and Fab-bound ligand can bind to the capture antibody. The biotinylated secondary antibody reagent (B3, red) can also bind in the presence of the Fab, thus allowing the detection of total (free and Fab-bound) ligand.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.