Figure 2. Reduction of Total Interdependence during Movie Watching for the Within-Network Interaction.
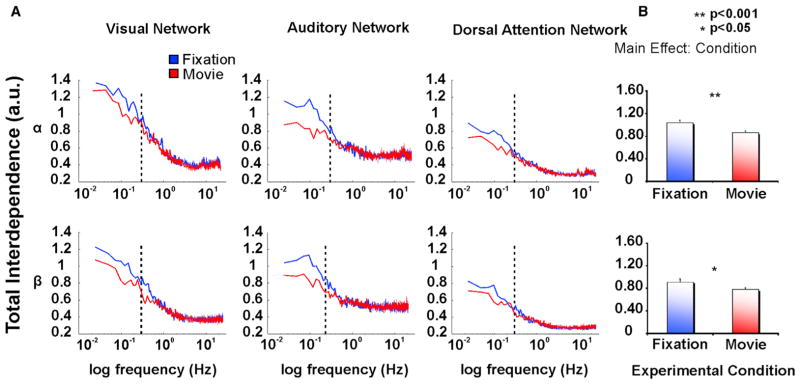
(A) Total Interdependence on a semilog scale in the α and β BLP for the visual (left column), auditory (middle column), and dorsal attention (right column) Network obtained from nodes of each network and averaged over runs, separately for fixation (blue line) and movie (red line). In both α and β bands, the internodal within-network interdependence is stronger at lower (<0.3 Hz, dotted lines) than higher frequency bands, with a maximum peak at about 0.1 Hz during fixation. Movie watching decreases the internodal interaction in each network.
(B) The statistically significant reduction of the total interdependence during movie among nodes within each network with respect to fixation, as revealed by the significant effect condition. Error bars indicate ± SEM.
