Figure 5.
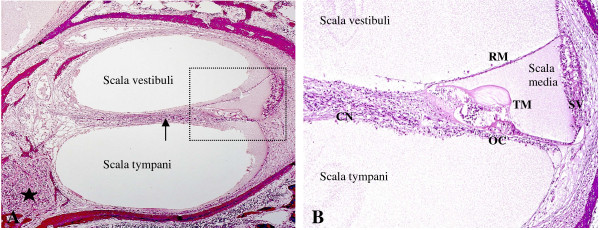
Human fetal cochlea at 21 weeks gestation. A) Cochlear turn: the cochlea is divided in three tubular compartments: scala vestibuli, tympani and media (detail). The first two contain perilymph, a liquid with an ionic composition similar to extracellular fluids. The scala media contains endolymph, with a positive potential of 80 mV, the endocochlear potential, essential for stimulating the sensory cells of the Organ of Corti. The signals generated travel along the cochlear nerve fibers (arrow) to the spiral ganglion (star) and then through the auditory pathway. B) Scala media: the scala media contains the Organ of Corti (OC), composed of sensory cells innervated by the cochlear nerve (CN) and stimulated by the tectorial membrane (TM) according to endolymph waves. Endocochlear potential within the scala media is mainly maintained by the stria vascularis (SV) with the contribution of the Reissner’s membrane (RM).
