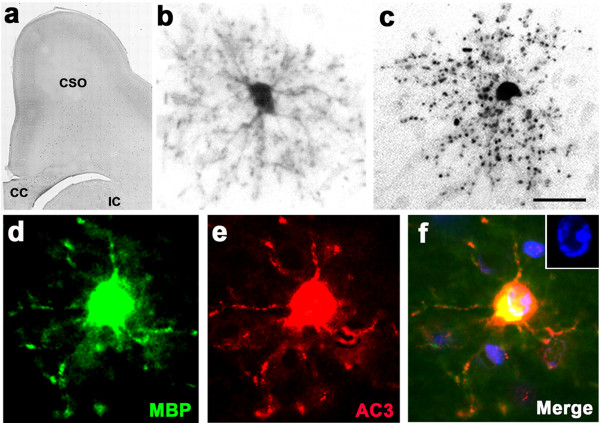
Figure 2.
Section from the rostral forebrain of an alcohol-exposed G120 fetal NHP brain stained with antibodies to MBP, which detects myelinated axons and OLs that contain MBP in their cytoplasm. Panel (a) is a low magnification overview showing that at this rostral level, there is no evidence for myelination of developing axonal tracts coursing through WM regions underlying the frontal cortex (FC), such as the centrum semi-ovale (CSO), corpus callosum (CC), and internal capsule (IC). However, there are many MBP-positive promyelinating OLs visible at higher magnification. Panel (b) shows the typical appearance of a normal promyelinating OL that contains enough MBP in its cytoplasm to allow the entire cell to be visualized by MBP staining. At this stage, the OL displays numerous radially oriented processes that have fluffy membranous extensions. Panel (c) presents the appearance of an MBP-stained promyelinating OL that is undergoing apoptotic cell death following alcohol exposure. The processes have disintegrated and present as a halo of MBP-positive debris surrounding a condensed cell body. Panels (d), (e), (f) illustrate an MBP-positive promyelinating OL that co-labels with AC3, signifying that it is dying by apoptosis. An abnormal nuclear chromatin pattern revealed by DAPI counterstaining (blue, Fig f inset) confirms the apoptosis diagnosis. Scale bar in (c) represents 750 μM in (a), 20 μM in (b) and (c), and 12 μM in (d-f).