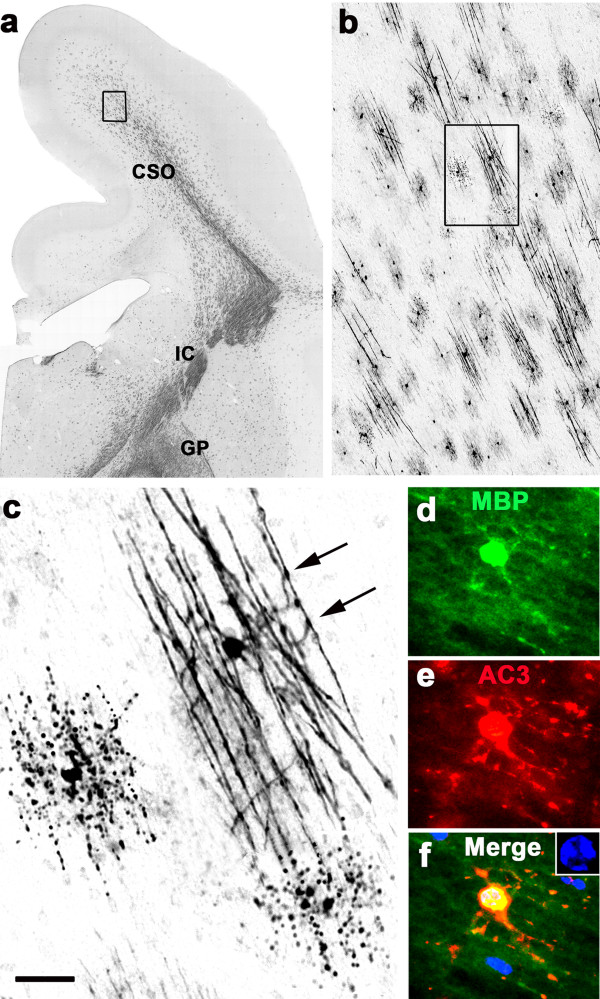
Figure 3.
Section at a mid-rostrocaudal level of an alcohol-exposd G120 fetal NHP brain stained with antibodies to MBP. Panel (a) is an overview showing that several regions at this rostrocaudal level, including centrum semi-ovale (CSO), internal capsule (IC) and globus pallidus (GP), are undergoing myelination. The boxed region in (a), shown at higher magnification in (b), depicts the typical appearance of early myelination, which is characterized by numerous small patches of axons, each of which is attended by an MBP-positive OL that is actively myelinating that patch. The box in (b), magnified in (c), shows one such patch consisting of segments of about 10 axons being contacted by the processes of a single OL that is wrapping sheets of MBP-positive membranes around them. Note the intense MBP staining at the points of contact between OL processes and axonal segments (arrows). At the middle left and bottom right of panel (c) are MBP-positive degenerating OLs that committed to cell death after having transferred MBP to a patch of axonal segments. Note the linear configuration of the MBP-positive breakdown products that conforms to the layout of an axonal patch. Panels (d, e, f) are double-stained immunofluorescent images documenting the typical appearance of an MBP-positive myelinating OL that co-labels for AC3, signifying that it is undergoing apoptotic cell death, which is confirmed by DAPI counterstaining revealing an abnormal nuclear chromatin pattern (blue, inset panel f). Note that the MBP positive processes of this cell contact and appear to be confluent with multple axonal segments, and these same processes are flooded with AC3, even along the surface of the axonal segments. Scale bar in (c) represents 1000 μM for (a), 100 μM for (b), 20 μM for (c) and 15 μM for (d,e,f).