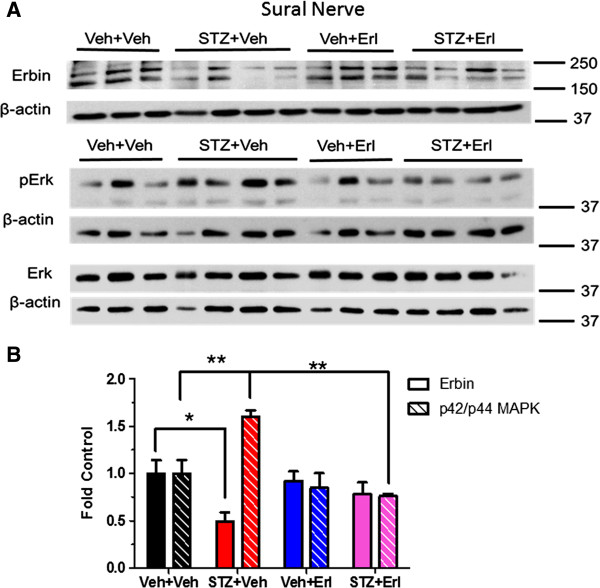
Figure 8.
Inhibition of Erb B2 with erlotinib suppressed diabetes-induced p42/p44 MAPK pathway activation in sural nerves. (A): Sural nerves were isolated from vehicle or erlotinib-treated control and diabetic mice (n = 3–4 per group) at week 21. Protein lysates were prepared and erbin levels and p42/p44 MAPK (pErk) levels were determined by immunoblot. (B): Quantification demonstrated a significant decrease of erbin and an increase in p42/p44 MAPK activation in vehicle-treated diabetic mice. Erlotinib treatment suppressed p42/p44 MAPK activation in erlotinib-treated diabetic mice (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01).