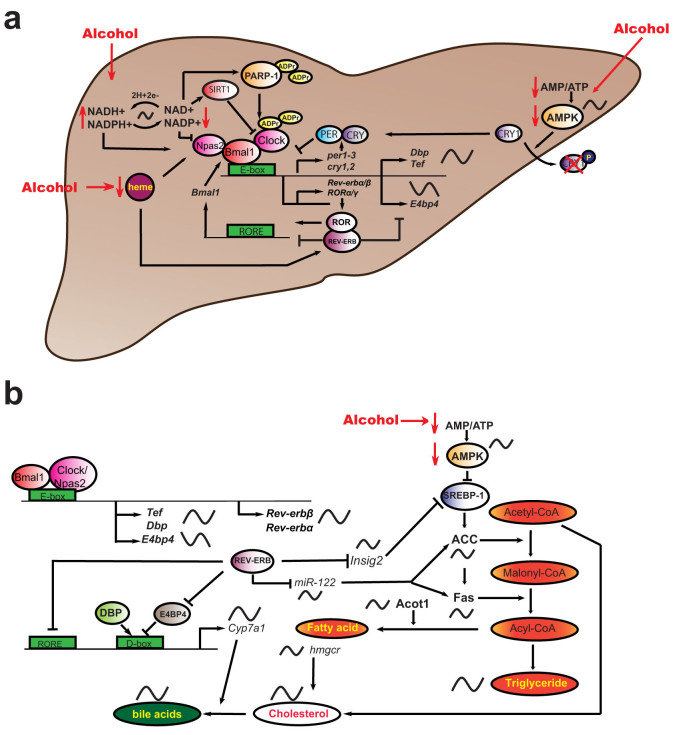
Figure 6. Model for effect of alcohol on hepatic circadian and metabolic systems.
(a) Alcohol affects the circadian system through three main pathways: 1) alteration of intracellular redox state via NAD/NADH, thereby influencing activity of positive TTFL components. The CAF effect is partly mediated through altering the redox state, and leading to a decrease in the NAD/NADH ratio and in an anti-phase shift in its diurnal profile. The clock is regulated by the NAD/NADH ratio, whereby NADH can enhance DNA-binding activity of NPAS2:BMAL1 heterodimers, and NAD+ inhibits DNA-binding activity23. NAD+ regulates the activity of the deacetylase SIRTUIN1, thereby altering CLOCK:BMAL1-dependent transcription28,29. Intersecting feedback loops also result in NAD+ being under clock regulation28,29. NAD+ also acts as an adenosine diphosphate (ADP) ribose donor for poly-ADP ribose-polymerase-1 (PARP-1), which can bind to the CLOCK:BMAL1 heterodimer and poly (ADP ribosyl)ate CLOCK30. Hence, low NAD/NADH ratio is predicted to cause an increase in CLOCK:BMAL1 on E-box binding and increase transcriptional activity of target clock genes (per2, per3, cry2, Rev-erbα/β) and CCGs (Dbp, Tef, Hes6); 2) reducing heme levels and thus affecting the transcriptional activity of clock components NPAS2 and REV-ERBα/β, which contain heme-binding motifs34,35. Hepatic heme concentration is reduced in rats chronically fed with alcohol37; and 3) cellular energetics via AMP/ATP ratio, in turn affecting CRY1 degradation. CAF has been shown to reduce the activity and phosphorylation of adenosine monophosphate activated protein (AMPK)38. AMPK is under rhythmic regulation and can phosphorylate CRY1, leading to CRY1 degradation39. (b) Downstream clock targets include enzymes involved in FA synthesis, which eventually results in altered regulation of TGs, cholesterol and BA synthesis. Rev-erbα participates in the transcriptional regulation of liver specific miR-122, which was differentially regulated in our study, and which regulates Fas and ACC8,25. Additionally, DBP and TEF contribute to the circadian transcription of Acot140. REV-ERBα can also regulate circadian BA and lipid homeostasis via cyclic expression of Insig2 and its subsequent action on SREBP activity41. CYP7A1 is the rate-limiting enzyme for synthesis of bile acids, and its expression is regulated by DBP and REV-ERBα/β. Rhythmically expressed components are indicated by sinusoidal lines.