Figure 4.
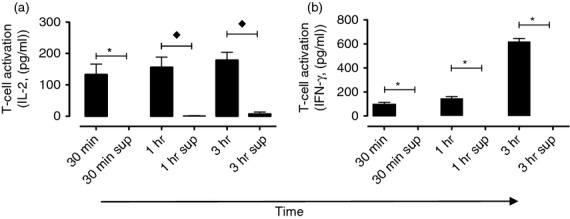
Contact-dependent, immobilized aggrecan acquisition by antigen-specific B cells leads to efficient CD4+ T-cell differentiation and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) production. T-cell receptor (TCR)-5/4E8 CD4+ T cells were cultured either with A20-agg B cells that had previously been incubated (for times shown) in wells containing immobilized aggrecan (im-agg; established with 10 nm biotinylated aggrecan) for 72 hr. In addition, TCR-5/4E8 CD4+ T cells were also cultured (72 hr) with fresh A20-agg B cells and supernatants (sup) that were removed (after times shown) from wells containing im-agg but lacking B cells. Levels of (a) interleukin-2 (IL-2) or (b) IFN-γ present in assay supernatants were determined as described in the Materials and methods. Mean cytokine levels (± SEM) are shown from each time-point from three independent experiments. Time-points where the mean cytokine levels produced following T-cell incubation with A20-agg B cells previously incubated with im-agg were significantly (P < 0·05) different from those following T-cell incubation with fresh A20-agg B cells and supernatants removed from im-agg (sup) (calculated using one-sample (⋆), or two-sample (♦) unpaired t-tests) are indicated. (IL-2 in wells containing T cells, A20-agg and sup removed from im-agg after 30 min was below detectable levels. Similarly, IFN-γ in wells containing T cells, A20-agg and sup removed from im-agg after 30 min, 1 hr and 3 hr was below detectable levels).
