Figure 2.
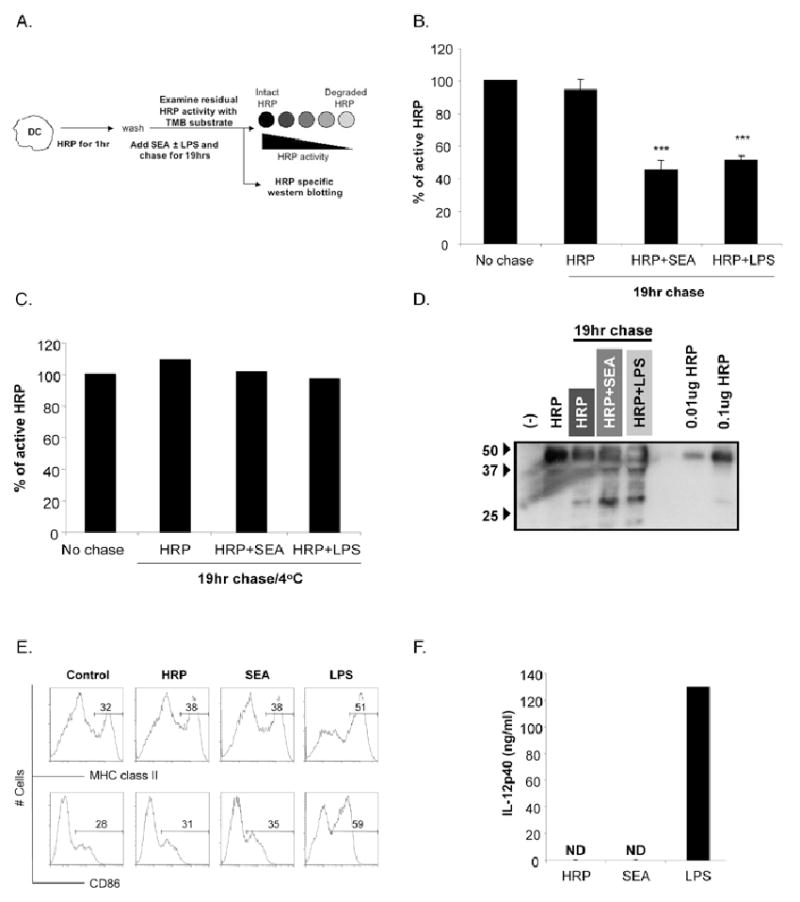
Activation of immature DCs with SEA induces antigen processing in the absence of phenotypic maturation. A. Protocol for assaying antigen processing in DCs following pulsing with HRP. DCs were pulsed with LPS-depleted HRP for 1hr prior to extensive washing to remove excess extracellular HRP. Cells were then either harvested to calculate initial (no chase) activity of HRP, or chased in the presence of SEA or LPS for 19hrs before being harvested to determine intact HRP activity (19hr chase). The percentage of intact HRP remaining after 19hrs was calculated by comparing the level of HRP activity in immature (HRP only), SEA or LPS cells after 19hr chase to initial no chase HRP activity. B. Percentage of HRP activity remaining in immature DCs (HRP), SEA and LPS DCs after 19hrs chase. C. Percentage of HRP activity remaining in immature DCs (HRP), SEA and LPS DCs after 19hrs chase at 4°C. D. After 19hr chase, extracts from HRP-pulsed-immature, SEA and LPS activated DCs were electrophoretically separated, blotted and probed with Ab specific for HRP. Cells were pulsed with HRP for 1hr as described above and subsequently cultured for 19hrs in the presence of medium (HRP), SEA or LPS. Cells and supernatant were harvested after 19hrs and analyzed for surface expression of MHC class II and CD86 and IL-12p40 by ELISA. Significant differences by Student's t test (*** p<0.05), where data points represent mean value ± SEM of data from seven experiments.
