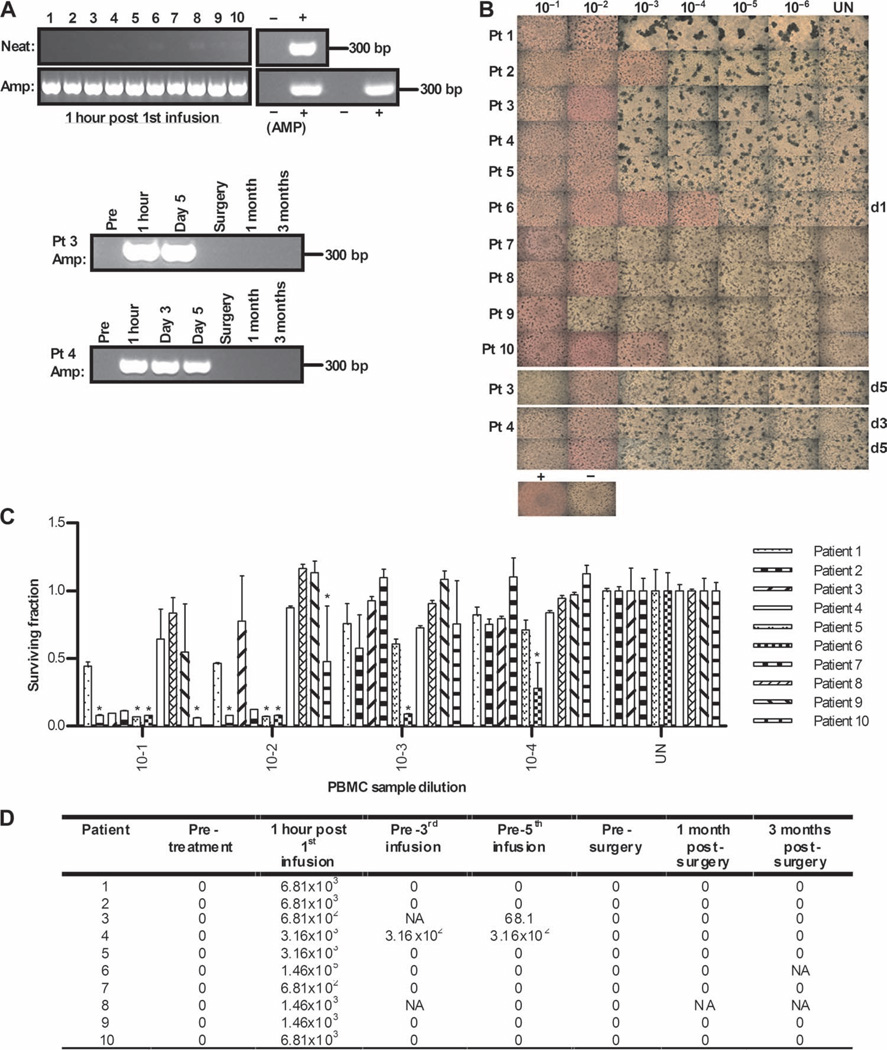
Fig. 3.
Despite circulating NABs, PBMCs transiently carry reovirus after infusion, which can replicate in and kill target cells in vitro. (A) Day 1 post-infusion PBMCs were assessed directly for reovirus RNA by RT-PCR (neat) or after an additional amplification step on L929 cells for 7 days (amplified). Reovirus RNA and RNase-free water were included as positive and negative controls, respectively, alongside a 1:10 dilution of stock reovirus or 5% DMEM incubated on L929 cells as amplified positive and negative controls (AMP). Later time points for patients 3 and 4 are also shown. (B) PBMCs were assessed for functional reovirus in a TCID50 assay. L929 cells were cultured with serial dilutions of PBMCs and observed 7 days later for CPE. Photomicrographs show results from day 1 post-infusion PBMCs for all samples and later time points for patients 3 and 4. Dilution (1:10) of stock reovirus or 5% DMEM (UN) was incubated on L929 cells as positive and negative controls, respectively. Rounded up cells and unused (red) media signify CPE. (C) Reovirus-induced cell killing by day 1 posttreatment PBMCs was further confirmed by MTT analysis. *P < 0.05 versus untreated control; error bars represent SEM. (D) Viral titers (TCID50/ml) from PBMCs over time (NA denotes samples unavailable for analysis).