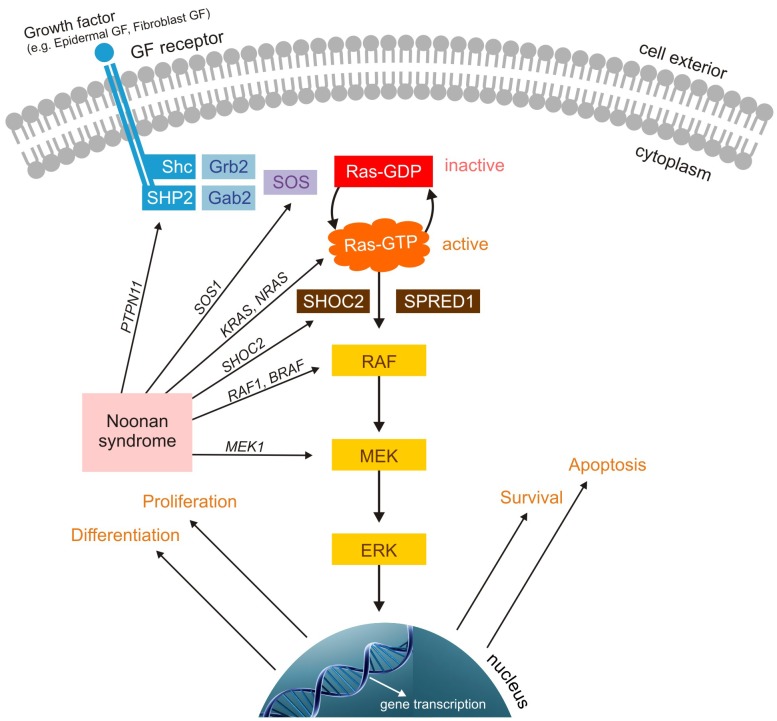
Figure 3.
RAS-mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Extracellular ligand such as growth factor (GF) binds to GF receptor and activates cytoplasmatic part of the receptor (a tyrosine kinase), which by phosphorylation enables binding with docking proteins such as GRB2. This protein forms a complex with sons of sevenless (SOS) guanine nucleotide exchange factor and activates it. Activated SOS removes guanosine diphosphate from RAS protein and activates it. Activated RAS protein then activates rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma (RAF) kinase, and RAF kinase subsequently activates MEK kinase (mitogen-activated protein [MAP] kinase kinase). MEK kinase finally activates mitogen-activated protein kinase MAPK, also known as extracellular signal regulated kinase. Mutations in genes controlling production of these signaling proteins, causing Noonan syndrome, are indicated (PTPN11, SOS1, KRAS, NRAS, SHOC2, RAF1, BRAF, MEK1).