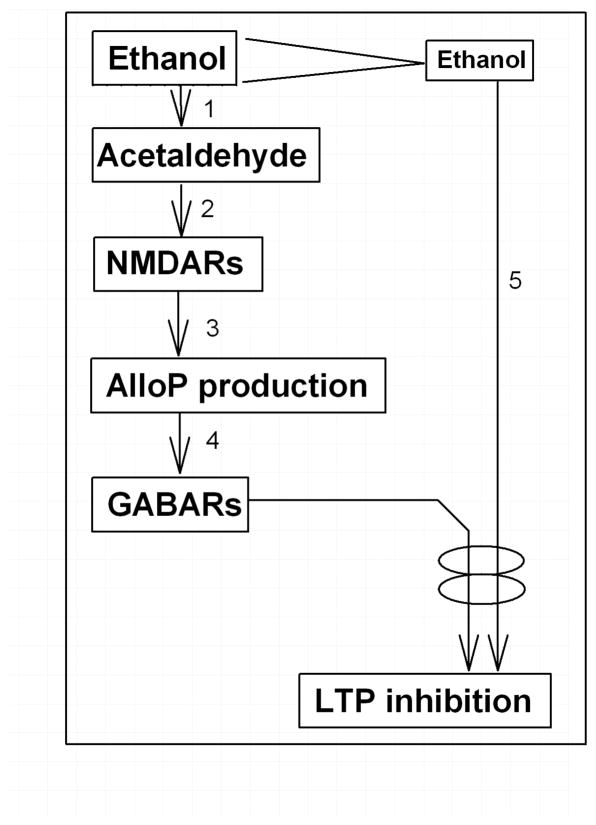
Figure 8.
A Scheme shows possible mechanisms for ethanol to inhibit LTP. 1. Only High concentrations of ethanol are metabolized into acetaldehyde via group III ADH. However, ADH can be activated by other substrates. 2. Acetaldehyde activates NMDARs through unknown fashion. 3. Activation of NMDARs activates TSPO resulting in synthesis of neurosteroids including alloP. This process is blocked by Finasteride. 4. Neurosteroids activate GABARs. 5. Activation of GABARs synergetically inhibits LTP induction with other various stressful conditions. These conditions include ethanol exposure even if the concentrations are moderate.