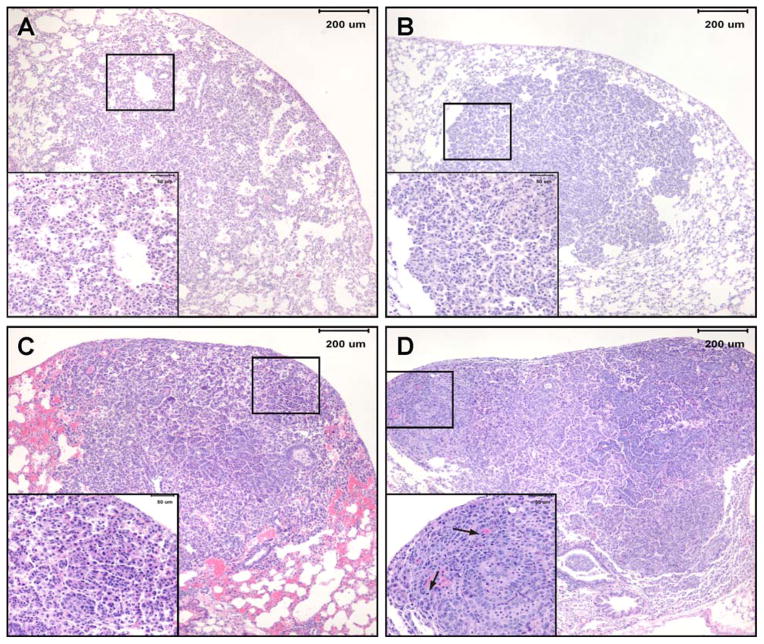
Figure 4.
Photomicrographs of lung lesions observed in NNK plus BaP-treated A/J mice lung. A, hyperplasia- a focal area of hypercellularity in the pulmonary parenchyma that consists of thickened alveolar walls covered by a single row of epithelial cells while maintaining alveolar architecture; B, adenoma- moderately or well-delineated, nodular area of pulmonary hypercellularity that is composed of a uniform population of cells; C, adenoma with cellular pleomorphism (aka adenoma with dysplasia and adenoma with progression)- adenoma in which a proportion of the tumor (at least 10 cells) or the entire tumor is composed of cells that have large cell and/or nuclear size, increased cytoplasmic-to-nuclear ratio, prominent nucleoli, and exhibit nuclear crowding and increased numbers of mitotic figures with no evidence of parenchymal invasion by pleomorphic cells; D, adenocarcinoma- variably delineated, usually highly cellular nodular or multinodular area in pulmonary parenchyma consisting of cells with large nuclei, increased cytoplasmic-to-nuclear ratio, anisocytosis, anisokaryosis, prominent nucleoli, moderate to high mitotic figure rate (including bizarre mitoses) and evidence of focal or multifocal invasion of parenchyma, airways or blood vessels.