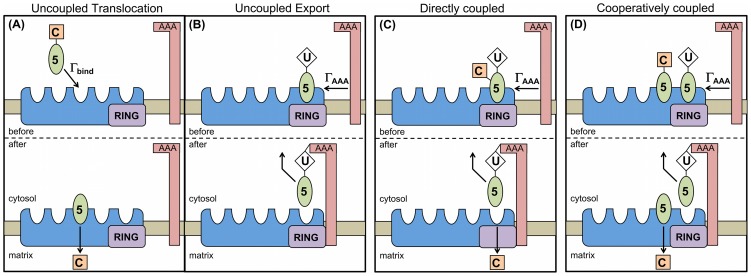
Figure 2. Illustration of translocation and export models and associated rates.
(A) PEX5 (green oval) associated with cargo (orange square) binds to available binding sites on a peroxisomal importomer (blue irregular shape) at a rate 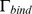 . In uncoupled translocation, associated cargo is translocated spontaneously after binding to the importomer. (B) If translocation is uncoupled, then export of ubiquitinated PEX5 by the AAA complex at rate
. In uncoupled translocation, associated cargo is translocated spontaneously after binding to the importomer. (B) If translocation is uncoupled, then export of ubiquitinated PEX5 by the AAA complex at rate 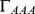 does not have a relationship with cargo translocation. (C) In directly coupled translocation, the cargo translocation occurs as the ubiquitinated PEX5 is removed from the importomer by the AAA complex at rate
does not have a relationship with cargo translocation. (C) In directly coupled translocation, the cargo translocation occurs as the ubiquitinated PEX5 is removed from the importomer by the AAA complex at rate 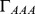 . The PEX5 is shown simultaneously both cargo-loaded and ubiquitinated — this figure is meant to be illustrative; see Methods for discussion. (D) In cooperatively coupled translocation, the removal of PEX5 by the AAA complex (
. The PEX5 is shown simultaneously both cargo-loaded and ubiquitinated — this figure is meant to be illustrative; see Methods for discussion. (D) In cooperatively coupled translocation, the removal of PEX5 by the AAA complex (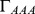 ) can only occur when coupled to the cargo translocation of a distinct PEX5-cargo in the same importomer. This always leaves at least one PEX5 associated with each importomer.
) can only occur when coupled to the cargo translocation of a distinct PEX5-cargo in the same importomer. This always leaves at least one PEX5 associated with each importomer.