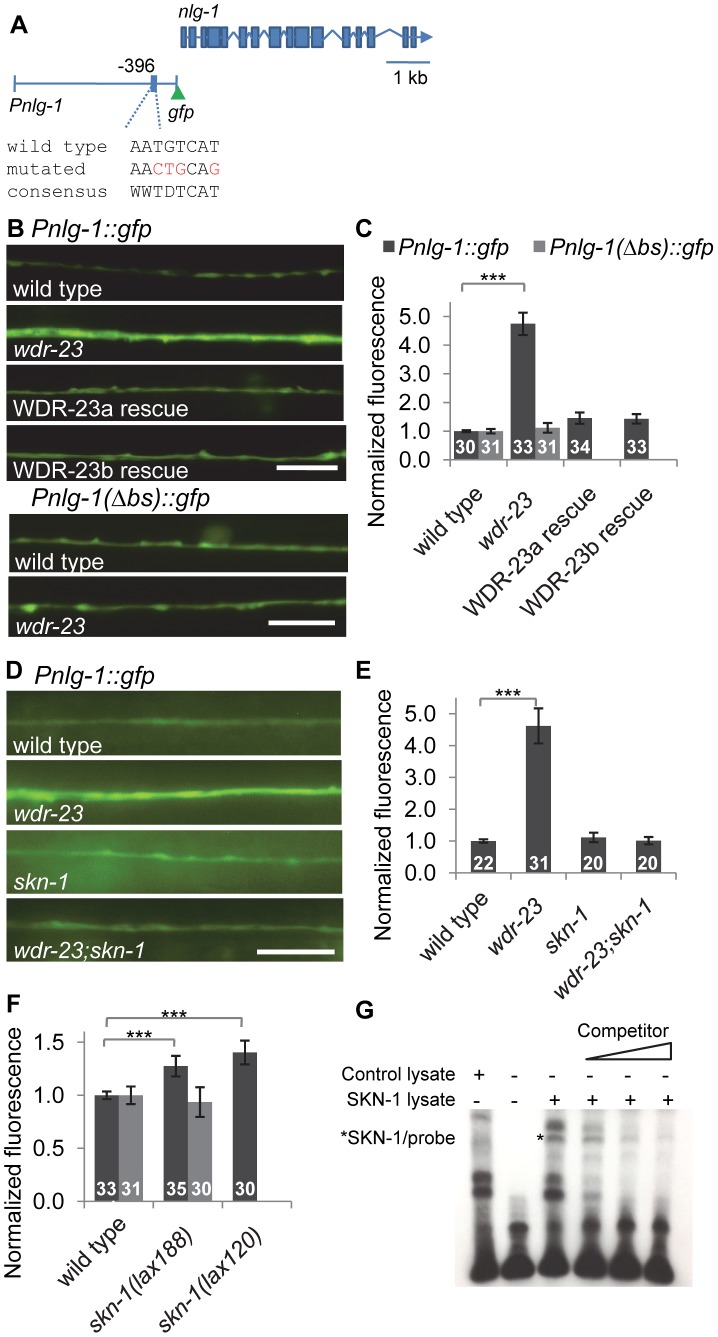
Figure 4. nlg-1 transcription is regulated by neuronal SKN-1.
A) Schematic of Pnlg-1::gfp reporters; vjIs47 and vjIs48 contain a 3.6 kb nlg-1 promoter driving gfp. Location of SKN-1 binding site and mutated site indicated. B) Top, Representative images of Pnlg-1::gfp (vjIs47) expression in the ventral cord of indicated strains. WDR-23a and WDR-23b rescues indicate isoform specific cDNA driven by the nlg-1 promoter (vjEx447 and vjEx436, respectively) and expressed in wdr-23 mutants. Bottom, Representative images of the extra-chromosomal transgene Pnlg-1(Δbs)::gfp (vjEx391) in the indicated strains. C) Quantification of Pnlg-1::gfp (vjIs47) and Pnlg-1(Δbs)::gfp (vjEx391) in indicated strains. Sample sizes indicated. Values normalized to wild type (vjIs47) or deleted binding site (vjEx391), respectively. D) Representative images of Pnlg-1::gfp (vjIs48) heterozygotes in indicated strains. skn-1 indicates zu67 loss of function allele, unless otherwise indicated. E–F) Normalized quantification of Pnlg-1::gfp (vjIs48) heterozygotes (E), Pnlg-1::gfp (vjIs48) homozygotes and Pnlg-1(Δbs)::gfp (vjEx756, F) in indicated strains. All nlg-1 reporters were imaged using the same microscope settings, and expression of reporters was similar between strains (total fluorescence vjIs48 in wild type animals: 3280.6±155.6; total fluorescence of vjEx756 in wild type animals: 2919.7±241.7). G) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay for binding of full-length SKN-1a to the consensus sequence at −396 bp. Lysate was either unprogrammed control or programmed to express SKN-1a. Competitor is 20, 100 and 200 fold molar excess of unlabeled probe. Scale bar represents 10 µm; error bars represent ±sem; ***p<0.001.