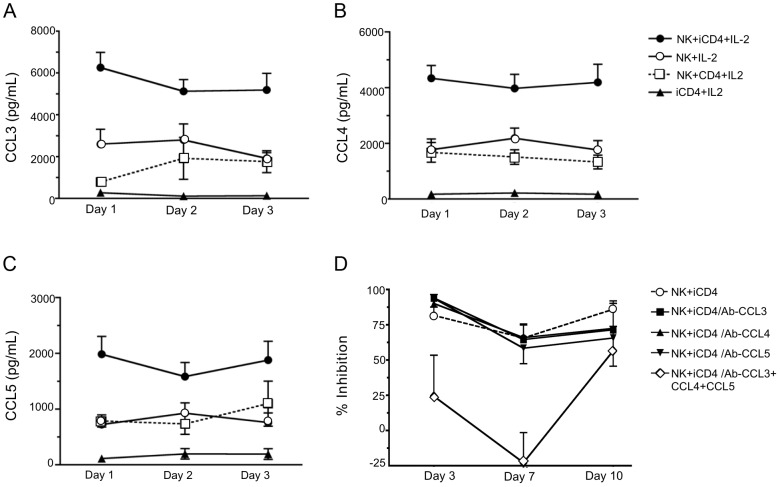
Figure 2. Infected CD4 T cells stimulate autologous NK cell to produce CC-chemokines.
Levels of CCL3 (A), CCL4 (B) and CCL5 (C) secreted into supernatants after days 1, 2 and 3 under various culture conditions were assessed by ELISA. Shown are results for NK cells cultured with infected CD4 cells (iCD4) at a 10∶1 ratio with 100 international units (IU)/ml of human recombinant IL-2 (IL-2) (NK+iCD4+IL-2, n = 33 observations), NK cells cultured with 100 IU/ml IL-2 (NK+IL-2, n = 24 observations), NK cells cultured with uninfected CD4 and 100 IU/ml of IL-2 (NK+CD4+IL-2, n = 9 observations) and iCD4 with 100 IU/ml IL-2 (iCD4+IL-2, n = 11 observations). Data points and error bars represent the mean and the standard error of the mean for the groups. Results were generated using subjects with the following KIR/HLA genotypes; *h/*y+B*57 (n = 4), 3DS1+*80I (n = 5), Bw6hmz (n = 4), *l/*x+B*57 (n = 4) and other KIR/HLA (n = 5). Samples were tested on up to 4 occasions in separate experiments. (D) Percent inhibition of viral replication on days 3, 7 and 10 of an NK cell autologous iCD4 cell co-culture (10∶1 ratio) in the absence of anti-CC-chemokine neutralizing antibodies (nAbs), in the presence of anti-CCL3, anti-CCL4 or anti-CCL5 nAbs, individually, or together. Results were generated using subjects with the following KIR/HLA gentotypes; *h/*y+B*57 (n = 2) and 3DS1+*80I (n = 5). Data points and error bars represent the mean and standard error of the mean of values for the groups.