FIGURE 1.
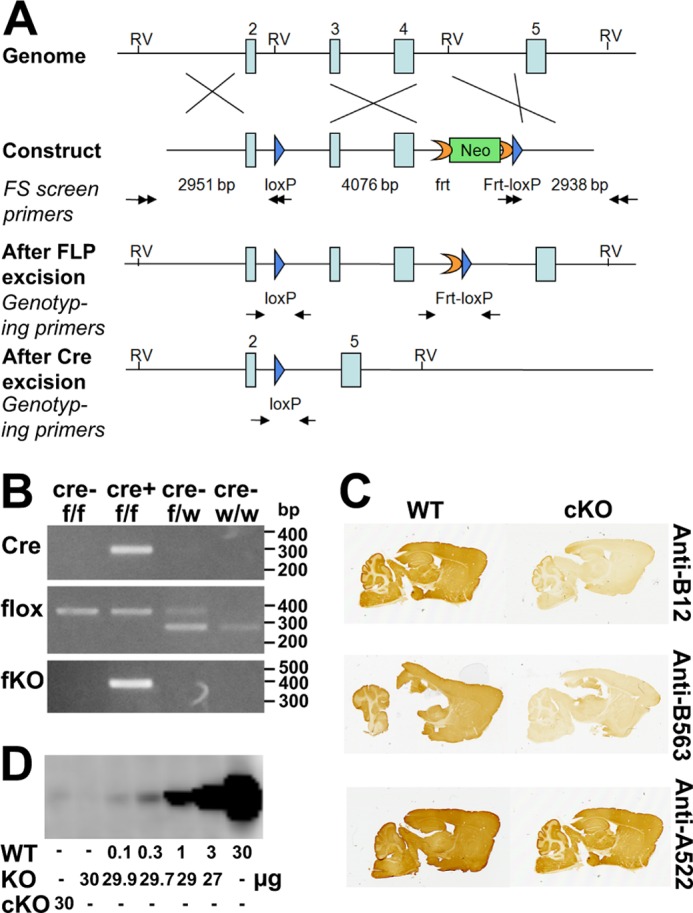
Generation and verification of the EAAT2-flox mice. A, generation of the EAAT2-flox mice. The gene-targeting construct contained exons 2–5 of the EAAT2 (Slc1a2) gene. A loxP sequence (blue arrow) was inserted into intron 2. An frt-PGKneo-frt-loxP cassette was inserted into intron 4, and an endogenous EcoRV (RV) site was deleted. The lengths of the homologous arms and of the floxed fragment are indicated below the construct. The black double arrows indicate the positions of the primers used for ES cell screening. The neomycin (Neo) cassette was removed in the EAAT2-flox mice generated from chimera × Rosa26FLP crossing. The genotyping primers are indicated by black arrows in the “After FLP excision” and “After Cre excision.” After Cre excision, the DNA encoding amino acid residues 53–187 is deleted. This region is essential for transport activity, and there will be no transport activity without it. Furthermore, the deletion causes the remaining sequences to be out of frame. B, PCR of genomic DNA of the brains from homozygote (f/f) or heterozygote (f/w) EAAT2-flox without (Cre−) or with (Cre+) Nestin11-Cre. PCR was performed to detect Cre, flox (loxP sites), and the recombination after Cre excision (fKO) as indicated. Note that when Cre is present the fKO allele emerges. Also note that the wild-type allele has lower molecular mass than the floxed allele, explaining why the there are two band in the heterozygous animals. C, peroxidase labeling of parasagittal brain sections from EAAT2-flox (WT) and conditional knock-out (cKO) mice with antibodies to the N terminus (Anti-B12; Ab360; 0.3 μg/ml) and the C terminus (Anti-B563; Ab355; 0.1 μg/ml) of EAAT2. Anti-A522 antibodies (Ab314; 0.1 μg/ml) to the C-terminal part of EAAT1 were used as a positive control. D, immunoblot analysis of the wild-type (WT) and conditional knock-out forebrain membrane fractions with antibodies to EAAT2 (Anti-B12; Ab360; 0.2 μg/ml). The WT tissue extracts were diluted in extracts from the conventional knock-out (KO) (27) to keep the total amount of protein constant at 30/per lane. Note that 30 μg from cKO gave a signal that was slightly weaker than that obtained after 1:300 dilution of the WT extract with KO extract.
