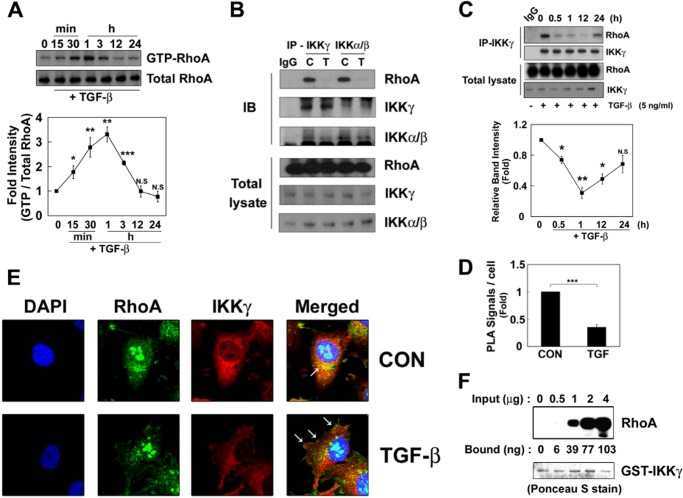
FIGURE 1.
RhoA interacts with the IKK complex. A, RAW264.7 cells were incubated with 5 ng/ml TGF-β1 at 37 °C, and GTP-RhoA levels were determined. B, the cells were treated TGF-β1 for 3 h. IKKα/IKKβ and IKKγ were immunoprecipitated with an anti-IKKγ antibody for 2 h at 4 °C, and then their co-precipitation with RhoA was determined by Western blot. C, control; T, TGF-β1 treatment. C, RAW264.7 cells were incubated with TGF-β1, and IKKγ was immunoprecipitated. The bound RhoA were analyzed by Western blot. Intensity of RhoA was quantified by densitometry (lower panel). D, RAW264.7 cells were treated with TGF-β1 for 1 h, and the interaction between RhoA and IKK was visualized in situ using a proximity ligation assay (PLA). The results are given as the means ± S.E. of three independent experiments (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001). E, HeLa cells were treated with TGF-β1 for 1 h, and RhoA (green), IKKγ (red), and nuclei (blue) were visualized. Arrows indicate RhoA localization in the membrane. F, GST-IKKγ (1 μg of protein)-Sepharose 4B beads were incubated with 0.5–4 μg of purified M-RhoA for 2 h at 4 °C, and RhoA bound to GST-IKKγ was detected by Western blot. The amount of RhoA bound to IKKγ was calculated from the control standard curve. GST-IKKγ was detected with Ponceau S staining. CON, control; IB, immunoblot.