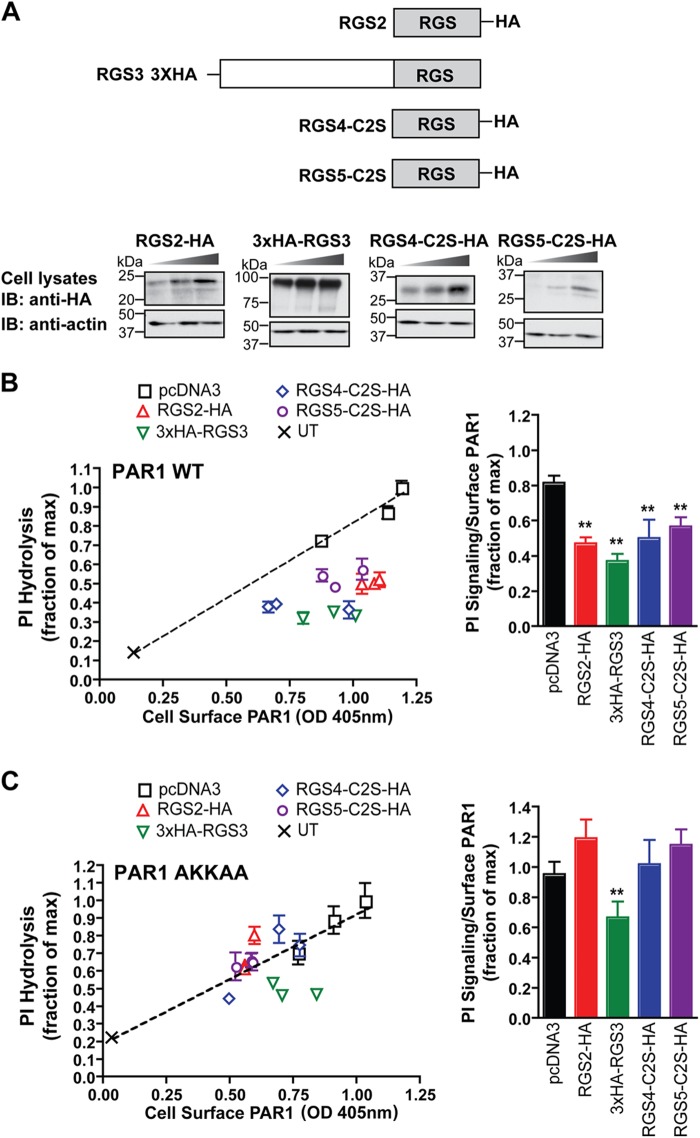
FIGURE 6.
Activated PAR1 signaling is negatively regulated by the R4 family of RGS proteins. A, domain structure of the HA-tagged R4 family of RGS proteins expressed in HeLa and endothelial cells. HeLa cells transiently expressing FLAG-tagged PAR1 WT and AKKAA mutant together with increasing amounts of HA-tagged RGS proteins, pcDNA3 vector, or untransfected (UT) control were either lysed or processed as described in B and C. Cell lysates were immunoblotted (IB) with anti-HA antibody to detect RGS protein expression or with anti-actin antibodies as a control. B and C, cells labeled with myo-[3H]inositol were incubated with 10 nm thrombin for 60 min at 37 °C, and [3H]IPs formed were measured. The data (mean ± S.D., n = 3) are representative of three independent experiments. The amount of PAR1 expressed on the cell surface (mean ± S.D., n = 3) for each transfected condition was determined by ELISA. The results are plotted as the fraction of [3H]IPs formed relative to the maximal response versus the amount of PAR1 expressed on the cell surface. The difference between the PI signaling normalized to receptor surface expression (mean ± S.D., n = 3) observed with PAR1 WT expressed alone in cells compared with cells coexpressing the various RGS proteins was significant as determined by single ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post hoc test (**, p < 0.01). However, only coexpression of RGS3 with the PAR1 AKKAA mutant caused a significant decrease in PI signaling compared with PAR1 AKKAA expressed alone as determined by single ANOVA and Tukey's HSD post hoc test (**, p < 0.01).