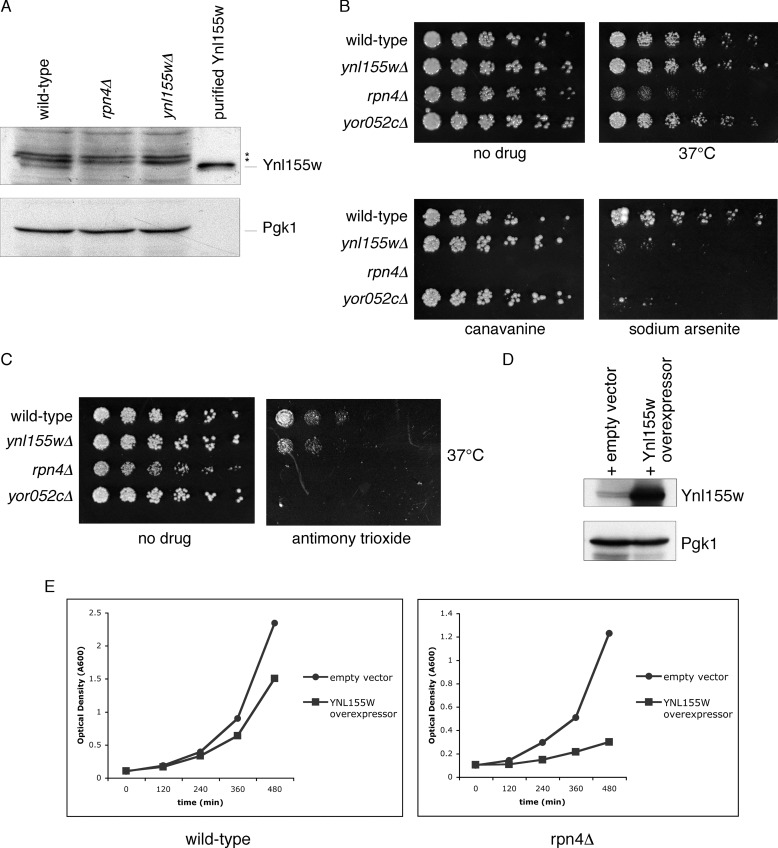
FIGURE 3.
A physiologic role for Ynl155w in the ubiquitin-proteasome system. A, Ynl155w protein levels are dependent on the transcription factor Rpn4. Whole cell extracts from wild-type, rpn4Δ, and ynl155wΔ cells were evaluated by SDS-PAGE immunoblot with antibodies against Ynl155w (upper panel) and Pgk1 loading control (lower panel). Recombinant purified Ynl155w is shown for reference. Asterisks, nonspecific bands. B, ynl155wΔ and yor052cΔ mutants are highly sensitive to arsenic. Three-fold serial dilutions of wild-type, ynl155wΔ, rpn4Δ, and yor052cΔ were spotted onto YPD plates containing no drug, the amino acid canavanine (1.5 μg/ml), and sodium arsenite (1.5 mm), and cultured at 30 or 37 °C for 2–6 days, as indicated. C, ynl155wΔ and yor052cΔ mutants are sensitive to antimony. Three-fold serial dilutions of wild-type, ynl155wΔ, rpn4Δ, and yor052cΔ were spotted onto YPD plates containing no drug or antimony trioxide (0.5 mm) and cultured at 37 °C for 2 days. D, a YNL155W overexpression plasmid increases Ynl155w protein levels. Upper panel, anti-Ynl155w immunoblot. Lower panel, anti-Pgk1 immunoblot (loading control). E, growth inhibition caused by YNL155W overexpression is enhanced in rpn4Δ cells. Wild-type and rpn4Δ cells expressing either an empty vector or a YNL155W overexpression plasmid were cultured in logarithmic phase growth at 30 °C, and culture optical density was assayed at the indicated time points.