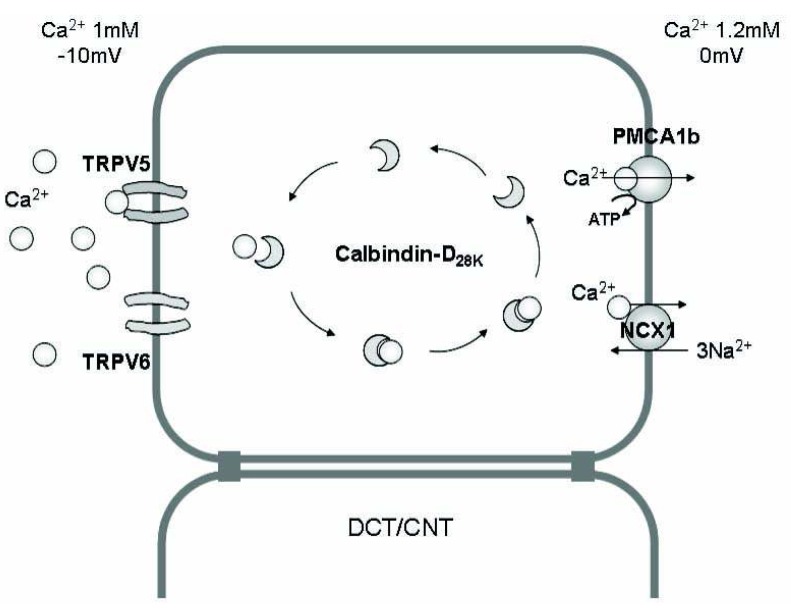
Fig. 2.
The mechanism of Ca2+ absorption in the renal epithelium. Transcellular Ca2+ reabsorption in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and connecting tubule (CNT) occurs by three steps; (i) entry of Ca2+ through the calcium channels [transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) 5, TRPV6] in the apical membrane, (ii) binding of Ca2+ with calcium-binding protein (calbindin) and diffusion in the cytoplasm (without significant change in the intracellular i[Ca2+]), and (iii) Ca2+ extrusion via an ATP-dependent Ca2+-ATPase (PMCA1b) or an Na2+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1) in the basolateral membrane.