FIG. 11.
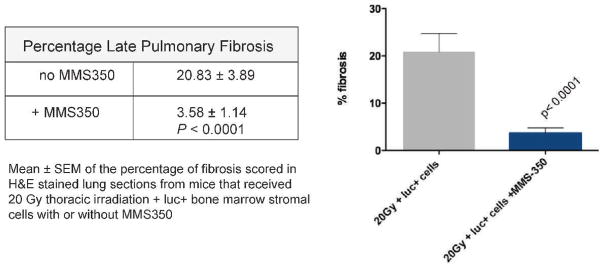
MMS350 in drinking water decreases late pulmonary fibrosis in thoracic irradiated C57BL/6NHsd mice. Twenty Gy irradiated pulmonary control mice (n =30) and a subgroup of mice treated with MMS350 in the drinking water daily beginning at day 100 (n =15) were injected with luc+ bone marrow cells at day 120 after irradiation. At 200 days after irradiation, lungs were removed and frozen sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Light microscopic quantitation of percentage of fibrosis in H&E stained sections was performed using ImageJ software as described in the Materials and Methods. For each animal, 2 slides with 2 fields/slide were scored, blinded, for a total of 4 fields/animal. Results are reported as mean ± SEM. Irradiated control mice had significantly more fibrosis than mice treated with MMS350 in their drinking water (P < 0.0001).
