Fig. 3.
SIM and STED superresolution images.
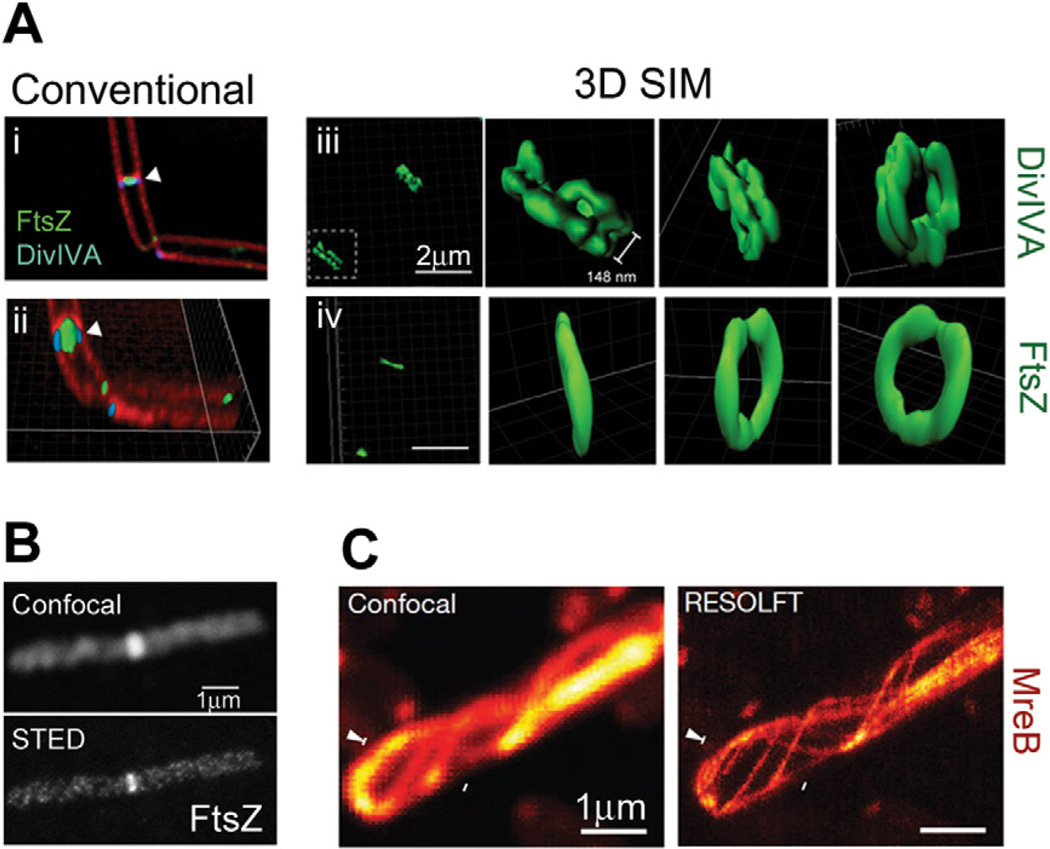
A. Ring structures formed by DivIVA and FtsZ in B. subtilis cells. Diffraction-limited images generated by conventional deconvolution (i and ii) show the proximity of DivIVA-GFP and FtsZ-YFP at dividing septa (membrane stained with FM4-64). 3D SIM reconstructions of DivIVA-GFP (iii) and FtsZ-GFP (iv), shown as surface representations, clearly show that DivIVA forms a double-ring structure while FtsZ forms a single-ring structure. Bars, 2 µm.
B. Images of Alexa647N–immunolabelled FtsZ in a B. subtilis cell. Superresolution imaging with STED (bottom) reveals discontinuous helical structures that are unresolvable by confocal microscopy (top). Bar, 1 µm.
C. Images of a live E. coli cell expressing rsEGFP-MreB. RESOLFT imaging (right) can resolve neighbouring MreB filaments that are indistinguishable by confocal microscopy (left). Bars, 1 µm. Images are reproduced from Eswaramoorthy et al. (2011) (A), Jennings et al. (2011) (B) and Grotjohann et al. (2011) (C).