Figure 4. Superposition of the Mtb CarD/RNAP complex structure with the bacterial elongation (EC) and initiation complex (IC) structures.
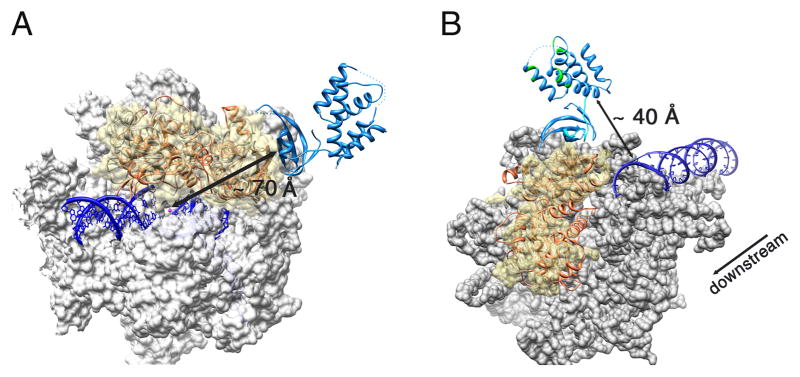
The Mtb CarD/RNAP complex is colored as previously (RpoBtr is orange and CarD is blue) (A) Superposition of the Mtb CarD/RNAP complex structure with the Tth RNAP EC structure (PDB ID: 2O5I). Tth RNAP is gray, the DNA duplex and DNA-RNA hybrid are dark blue, the active site Mg+2 is shown as a magenta sphere. The molecular surface of the α and β′ subunits is shown in gray, where the β1–β2 domains of the Tth RNAP are represented as ribbons under a transparent yellow surface. CarD binds to the solvent exposed surface of the β1 domain, ~ 70 Å away from the catalytic center. (B) Superposition of the Mtb CarD/RNAP complex structure with the Taq RNAP IC structure (PDB ID: 1L9Z). The molecular surface of the Taq RNAP is gray except for the β1–β2 domains which are represented as a transparent yellow surface. The DNA duplex is colored dark blue. The flexible α1 and eight residue loop of CarD are colored cyan. CarD’s DNA interacting patches as determined by EMSA are colored green. The direction of transcription is also indicated. The CarD C-terminal DNA interaction domain lies in close proximity to the downstream end of the dsDNA in the initiation complex (~40 Å).
