Figure 2.
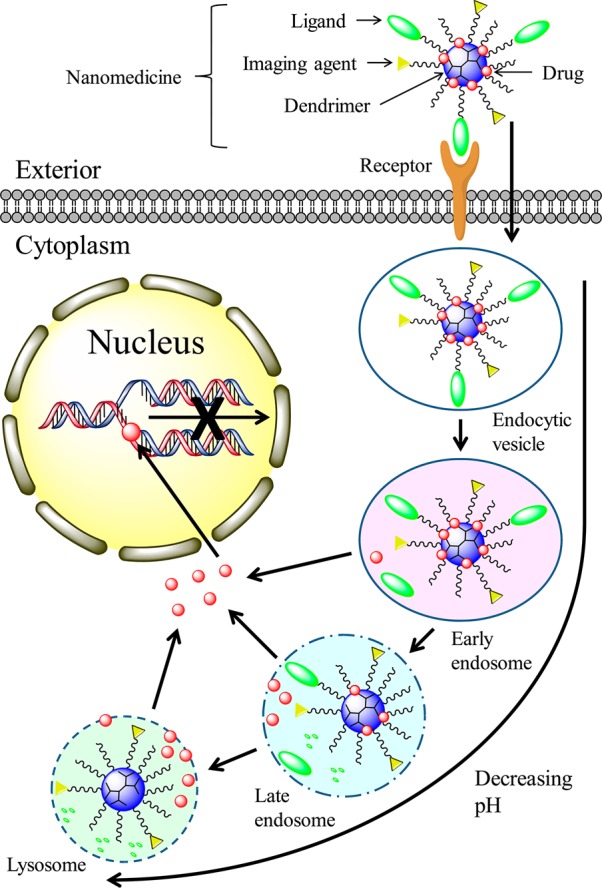
Mechanism of dendrimer intracellular delivery of therapeutics such as DOX and CPT. (1) Dendrimer nanomedicine is attracted to the cells by an electrostatic difference; (2) Ligand–receptor-mediated endocytosis occurs, and dendrimer nanomedicine is internalized into the cells; (3) reduction of the pH value from the endocytic vesicle to the lysosome triggers therapeutics to be cleaved from the dendrimer carrier and released into the cytoplasm; (5) released therapeutics diffuse into the nucleus, intercalate the DNA strand, and break the DNA chain to prevent its replication.
