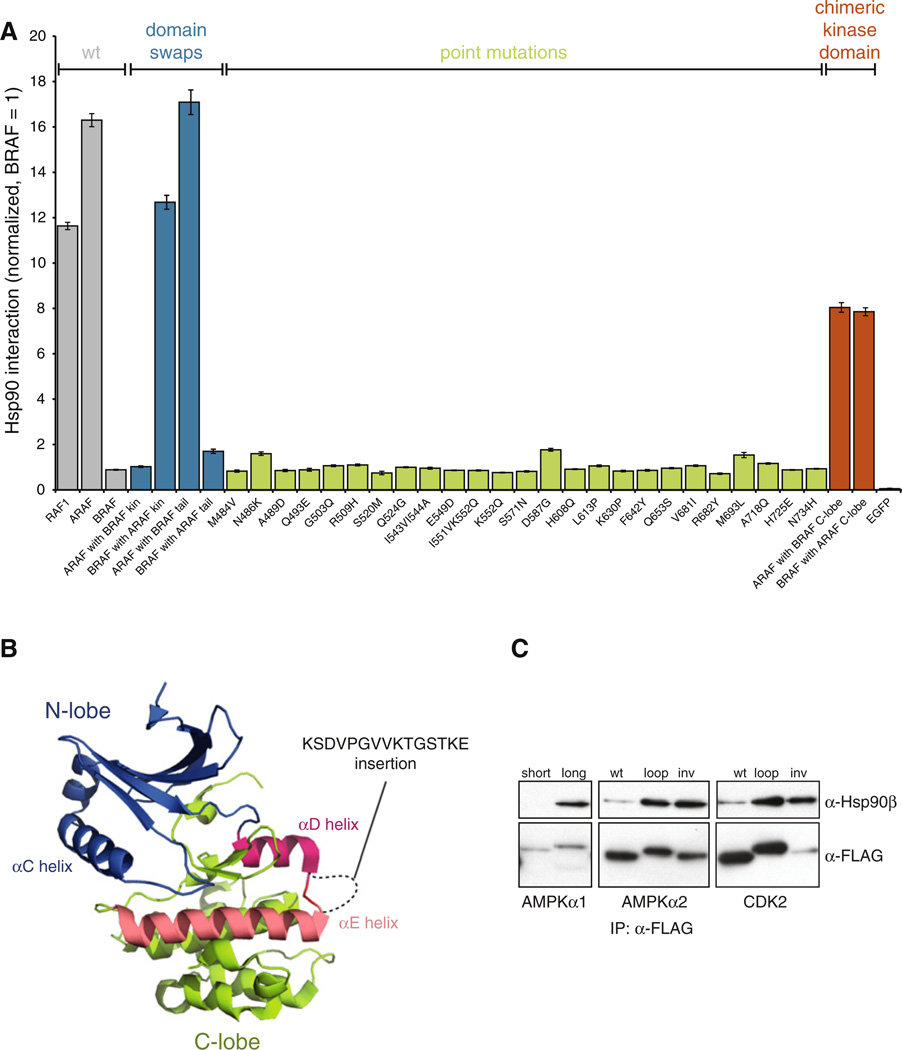
Figure 5. HSP90 Interaction Is Determined by a Distributed Set of Residues and Is Affected by Alternative Splicing.
(A) Multiple residues regulate ARAF interaction with HSP90. 3 × FLAG-tagged kinase constructs were transfected into Renilla-HSP90 cells and their interaction with HSP90 was measured with LU-MIER. Wild-type BRAF interacts weakly with HSP90, whereas RAF1 (CRAF) and ARAF are among the strongest HSP90 clients (gray). Constructs containing the kinase domain of ARAF but regulatory domains of BRAF interact strongly with HSP90 (blue), but single point mutations in BRAF do not confer robust interaction with HSP90 (green). Clones with chimeric kinase domains display intermediate phenotypes (orange). Error bars indicate SDs (n = 4).
(B) Location and the sequence of the alternatively spliced αD-αE loop in AMPKα1 (PRKAA1) are shown in the structure of the AMPKα2 isoform (PDB 2H6D). Kinase N-lobe is colored blue, C-lobe in green, αD helix in red, and αE helix in salmon pink.
(C) Alternative splicing of AMPKα1 regulates HSP90 association. 3 × FLAG-tagged kinase constructs were transfected into 293T cells and interaction with endogenous HSP90 was assayed by coimmunoprecipitation. AMPKα1 loop was inserted into AMPKα2 or CDK2 that do not have loops between the two helices. As a control, the DNA sequence encoding the loop sequence was also inserted inverted (inv) into the same location.
See also Figure S4.