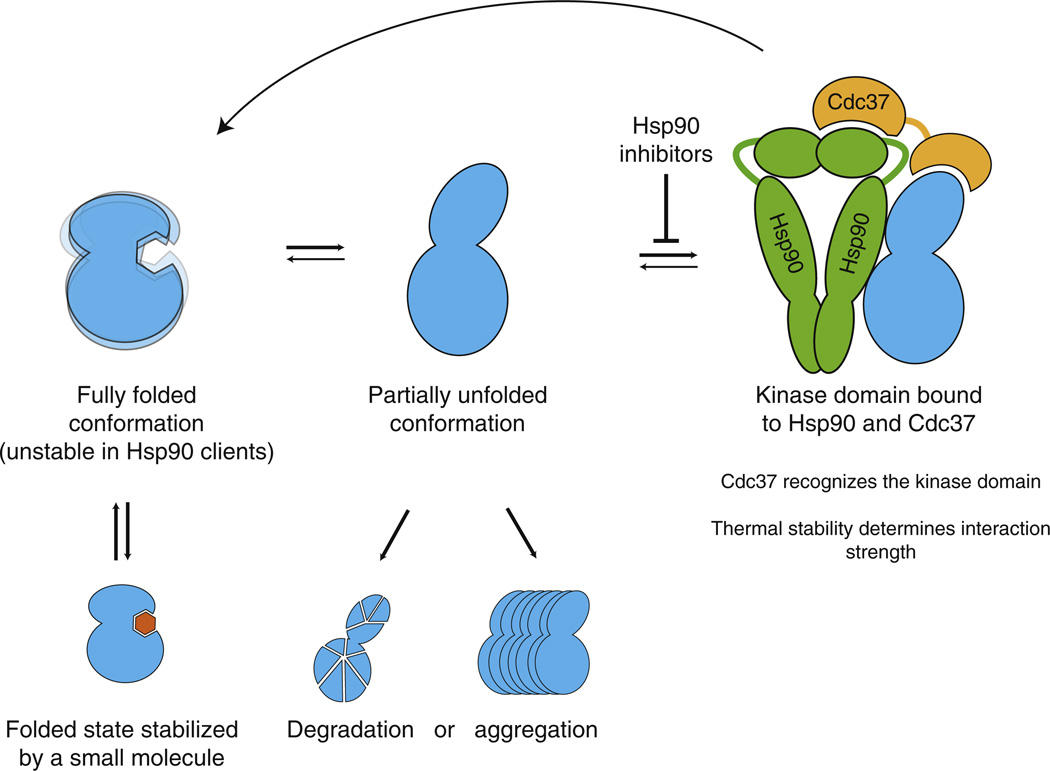
Figure 7. Model for HSP90::Kinase Interactions.
Kinase domains are in equilibrium between the fully folded and HSP90-binding competent conformations. CDC37 cochaperone recognizes the kinase fold and recruits kinases to HSP90. HSP90 binds the alternative kinase conformation and assists the kinase in adopting the fully folded conformation. Client kinases thus undergo repeated rounds of chaperoning, whereas nonclient kinases are stable when fully folded. Binding of an inhibitor to its target kinase increases the stability of the kinase fold and thus decreases HSP90 interaction. HSP90 inhibitors block the loading of the client to the chaperone, which leads to aggregation of the partially unfolded kinase or degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome system.