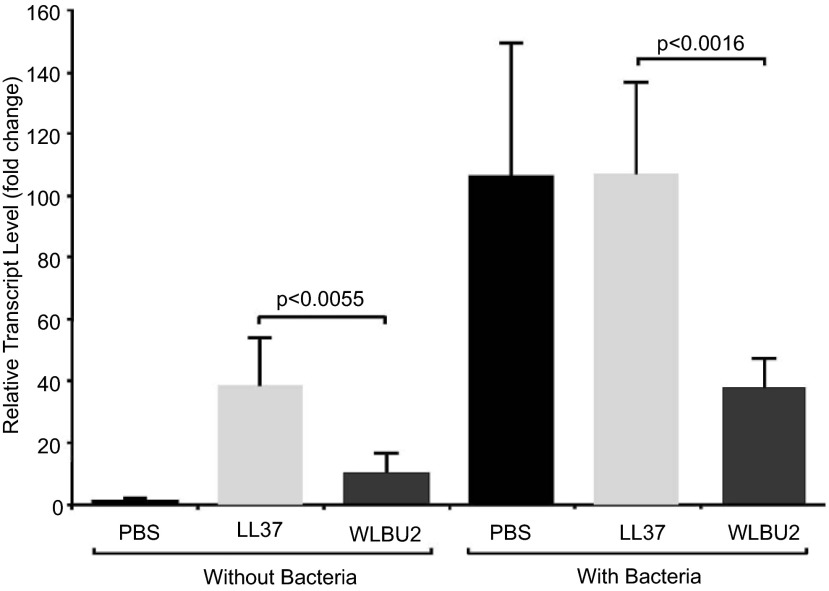
Figure 4. Intraperitoneal WLBU-2 suppresses IL-1β in lungs systemically exposed to P. aeruginosa (PA).
Wild-type C57BL/6 animals (n=5/group) received intraperitoneal injections of PBS or PA (1×10 6 cfu/mL), followed by intraperitoneal injections after 2h of PBS (black bars), LL-37 (4mg/kg, light grey bars), or WLBU-2 (4mg/kg, dark grey bars), with subsequent measurement by quantitative RT-PCR of IL-1β transcripts ( y axis, fold change in relative transcript level) from lung tissue harvested 24h post exposure. Data represent measurements performed in triplicate. In groups not receiving bacteria, LL-37 and WLBU-2-exposed animals showed an increase in IL-1β transcripts compared to PBS controls. In groups receiving PA, WLBU-2-exposed animals showed significant suppression of IL-1β ( p<0.005) compared to LL-37. These data suggest that the eCAP WLBU-2 may modulate proinflammatory cytokine release in the setting of acute infection.