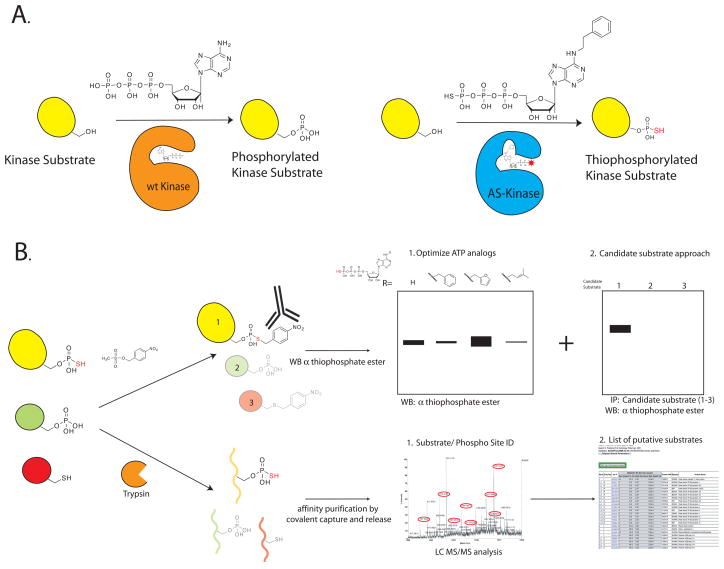
Figure 1.
Thiophosphopeptide purification scheme. A. wt kinase utilizes ATP to phosphorylate its substrates. In contrast, an engineered AS kinase has a new active site pocket that allows it to accept an unnatural bulky ATP analog. This “lock and key” allows the AS kinase to transfer the thiophospho group to its substrates. B. Detail of the two different affinity purification methods: The thiophosphorylated substrates are found in a background of phosphorylated and unlabeled proteins. In the first technique we react the thiophosphorylated proteins with a thiol specific alkylating agent that generates a bio-orthogonal thiophosphate ester. Labeled proteins are detected by using a thiophosphate ester specific antibody. In the second approach the lysate is first digested to generate tryptic peptides. Thiol containing peptides are captured by reaction with iodoacetyl agarose beads. All non-thiol containing peptides are then washed away, and the remaining peptides are treated with Oxone, which releases thiophosphate ester linked peptides by spontaneous hydrolysis.