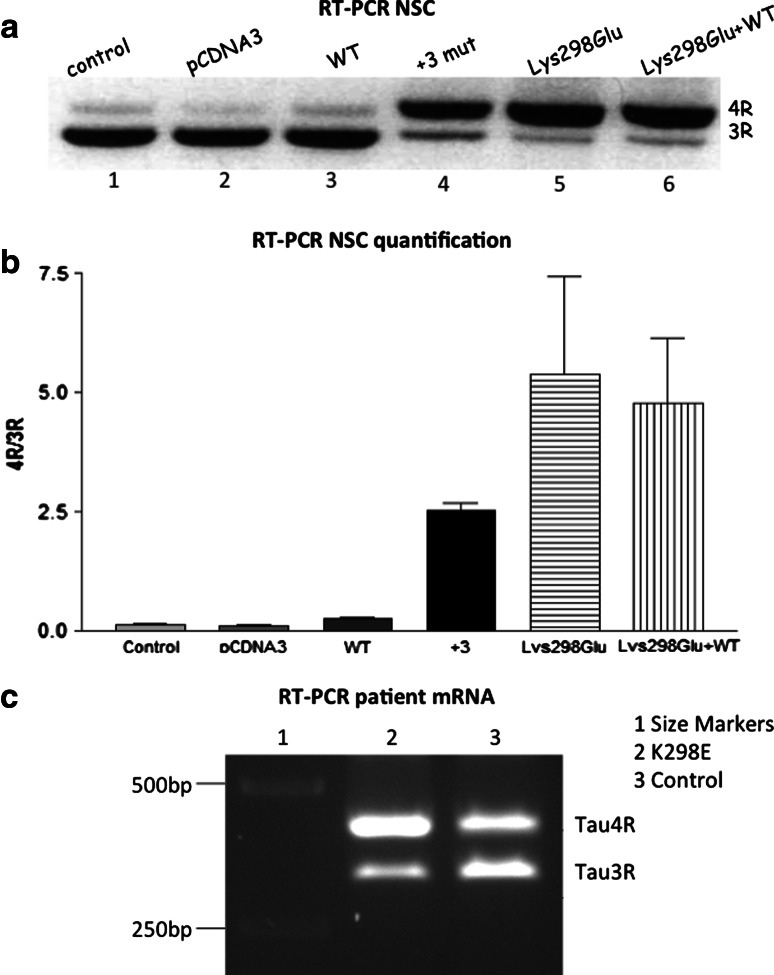
Fig. 2.
Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) analysis of tau mRNA expression in human neural stem cells transfected with a tau minigene and mRNA extracted from frontal cortex of the K298E patient. The tau minigene construct consisted of the pcDNA3 vector containing tau exons 9, 10 and 11, and the E10 flanking intronic sequences of minimal length for correct splicing. The splicing patterns of MAPT exon 10 in minigene transfected human neural stem cells (NSCs) are shown. a Untransfected human NSCs expressed high levels of 3R tau mRNA and low levels of 4R tau mRNA (lane 1) similar to cells transfected with the empty pcDNA3 vector (lane 2). Transfection with the wild-type tau minigene did not change the ratio between the two mRNAs (lane 3), with the expression level of 3R tau mRNA remaining predominant. When human NSCs were transfected with the minigene carrying the +3 MAPT mutation, the mRNA level of 4R tau increased (lane 4) and this also occurred after transfection with the minigene carrying the K298E mutation (lane 5). Co-transfection of wild-type and K298E minigenes did not alter the ratio between 3R and 4R tau isoforms mRNAs (compared to K298E alone), indicating that the K298E mutation has a dominant effect on exon 10 splicing (lane 6). The quantification shown in b was the result of three different transfection experiments and was performed using the Image J program (http://imagej.nih.gov/). c RT-PCR of mRNA extracted from frontal cortex of the K298E mutation patient showed a clear increase in 4R tau mRNA expression and a decrease in 3R tau mRNA expression compared to mRNA extracted from an age-matched control subject