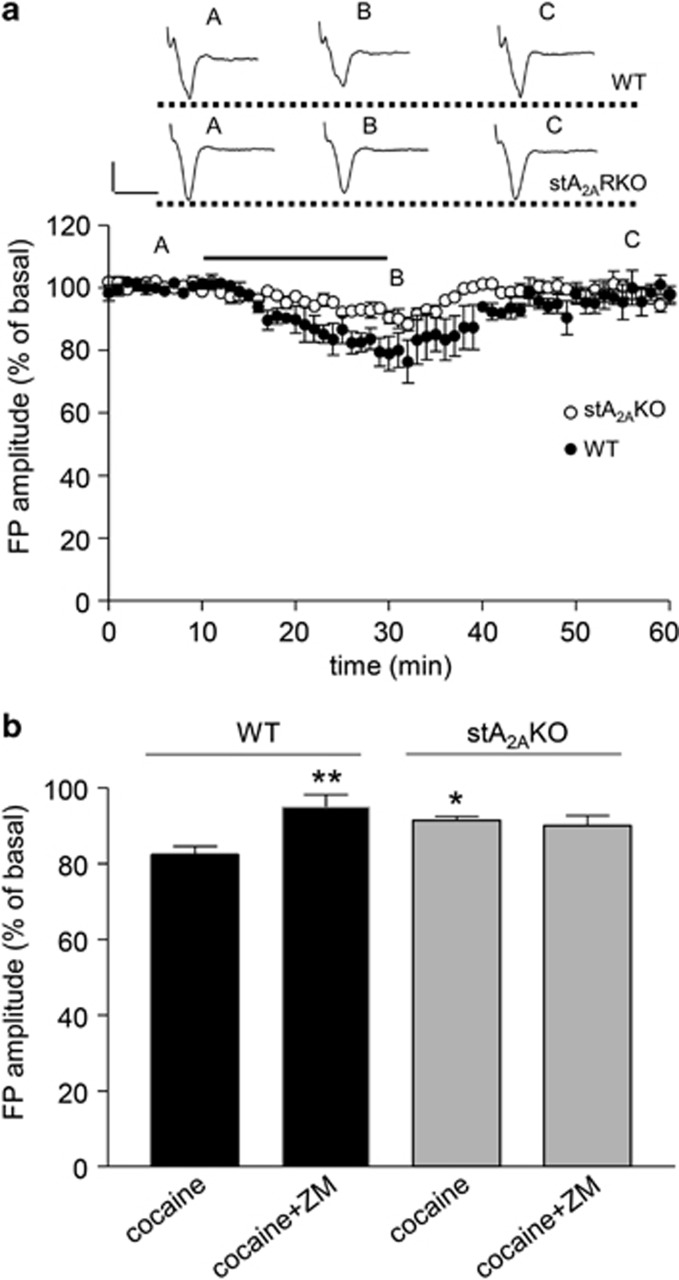
Figure 2.
Effects of cocaine on synaptic transmission in WT and stA2AKO mice. (a) cocaine-induced depression in FP amplitude is reduced in stA2AKO compared with WT mice. Each point represents the mean of three responses. Insets show FPs recorded in basal condition (A), 20 min after cocaine application (B) and at the wash-out (C), in WT and stA2AKO mice. The horizontal bar indicates the period of drug application. Calibration bars: 0.5 mV, 5 ms. (b) cocaine-induced reduction in FP amplitude in stA2AKO mice (N=6) is significantly reduced with respect to WT mice (N=6). ZM241385 prevents the effect of cocaine in WT mice (N=5) but not in stA2AKO mice (N=4). *p<0.05 and **p<0.01, significantly different from WT cocaine (the Kruskal–Wallis test). ZM=ZM241385.