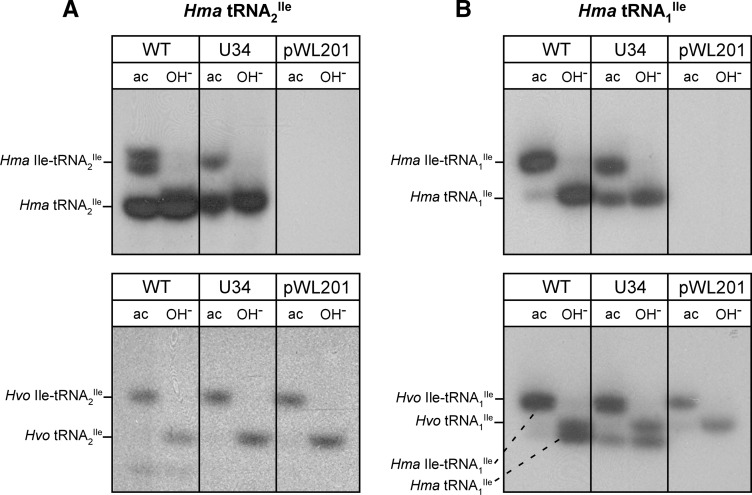
FIGURE 3.
State of in vivo aminoacylation of H. marismortui wild-type and U34 mutant tRNA2Ile (A) and wild-type and U34 mutant H. marismortui tRNA1Ile (B). Total tRNA was isolated under acidic conditions and analyzed by acid urea PAGE followed by Northern hybridization using probes specific for H. marismortui tRNA2Ile (A, top panel) and H. marismortui tRNA1Ile (B, top panel), respectively. The same blots were stripped and rehybridized using probes specific for the endogenous H. volcanii tRNA2Ile (A, bottom panel) and H. volcanii tRNA1Ile (B, bottom panel). Note that the H. volcanii tRNA1Ile-specific probe also picks up the overexpressed H. marismortui tRNA1Ile because of the high levels of overexpression of H. marismortui tRNAs and close sequence similarity between the overexpressed and the endogenous tRNA1Ile. (ac) tRNA isolated under acidic conditions; (OH−) tRNA after deacylation by base-treatment.