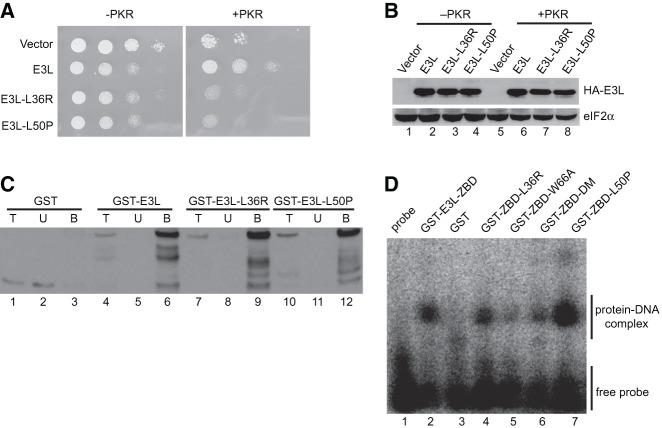
FIGURE 7.
Identification of point mutations in the ZBD of E3L that impair PKR inhibition, but not Z-DNA binding. (A) Growth phenotypes of E3L mutants identified through random mutagenesis. Transformants of yeast strains J110 (−PKR) or H2544 (+PKR) bearing empty vector pEMBLyex4 or plasmids that express the indicated HA-E3L derivatives under the control of a GAL–CYC1 promoter were grown to saturation, and 5 µL of serial dilutions (of OD600 = 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001) was spotted on SCGal (10% galactose) medium and incubated for 3 d at 30°C. (B) Immunoblot analysis of WCEs from yeast strains in panel A. Transformants were grown in SD medium at 30°C to OD600 ∼ 0.6, and then shifted to SCGal medium for 2 h. WCEs (5 µg) were fractionated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis using monoclonal antibodies against the HA epitope to detect HA-E3L (upper panel) and polyclonal antisera against yeast eIF2α as loading control (lower panel). (C) dsRNA binding. Purified GST or the indicated GST-E3L derivative was incubated with poly(I:C)-agarose for 1 h at 4°C. Bound proteins were collected by centrifugation and eluted by boiling in SDS sample buffer. Proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunoblot analysis using polyclonal anti-GST antiserum. (T) 5% of total protein used in the assay; (U) unbound (20%); (B) protein bound (20%) to the poly(I:C) agarose. (D) Z-DNA binding activity of E3L ZBD derivatives. The indicated GST-E3L-ZBD (residues 1–80) derivatives (5 µM) were incubated with the Z-DNA substrate [32P]-labeled d(C:5BrG)20 and assayed for Z-DNA binding ability by electrophoretic mobility shift assay.