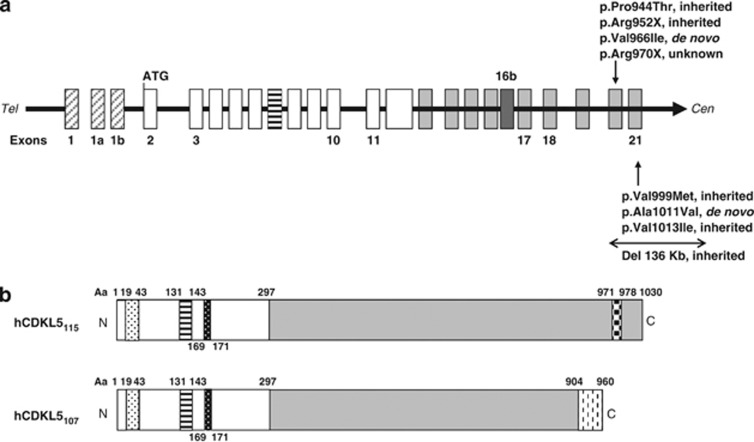
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of CDKL5. (a) Schematic representation of the human CDKL5 gene. CDKL5 exons are indicated by boxes. The three non-coding exons are shown hatched, and the new exon 16b is shown in dark grey. Mutations/variants in the 3′-end of CDKL5 reported to date are indicated corresponding to their location within the gene. (b) Human CDKL5 protein isoforms differing in the C-terminal region. Functional domains and signatures are indicated: ATP-binding domain (aa 19–43); serine threonine kinase active site (aa 131–143); TEY motif (aa 169–171), putative signal peptidase I serine active site (aa 971–978). CDKL5115 contains the primate-specific exons 19–21. In CDKL5107, 170 nucleotides of intron 18 are retained.