Figure 2.
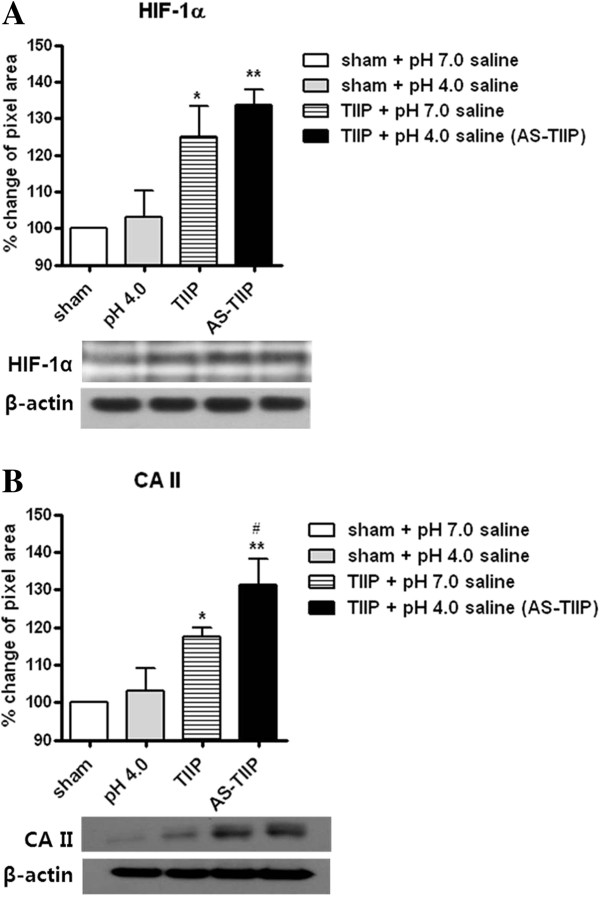
Western blot analysis of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and carbonic anhydrase II (CA II). HIF-1α (n = 5 in each group, day 3 post pH 4.0 saline injection) and, CA II (n = 4 in each group, day 3 post pH 4.0 saline injection) were quantitatively evaluated in sham and ischemic hind paw muscle lysates by western blotting. (A) The protein concentration of HIF-1α was significantly increased in the pH 7.0-treated thrombus induced ischemic pain (TIIP) group, and the protein concentration of HIF-1α was increased to an even greater extent in the pH 4.0 saline injected TIIP group (AS-TIIP); (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs sham + pH 7.0 saline). (B) The protein level of CA II was also significantly increased in pH 7.0-treated TIIP and AS-TIIP groups compared to the pH 7.0-treated sham group. pH 4.0 saline injection induced an additional increase in CA II expression in the AS-TIIP group compared to the pH 7.0-treated TIIP group. (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs sham + pH 7.0 saline and #P < 0.05 vs TIIP + pH 7.0 saline). Data are presented as percentage of change (%) relative to sham control. β-actin was used as a loading control.
