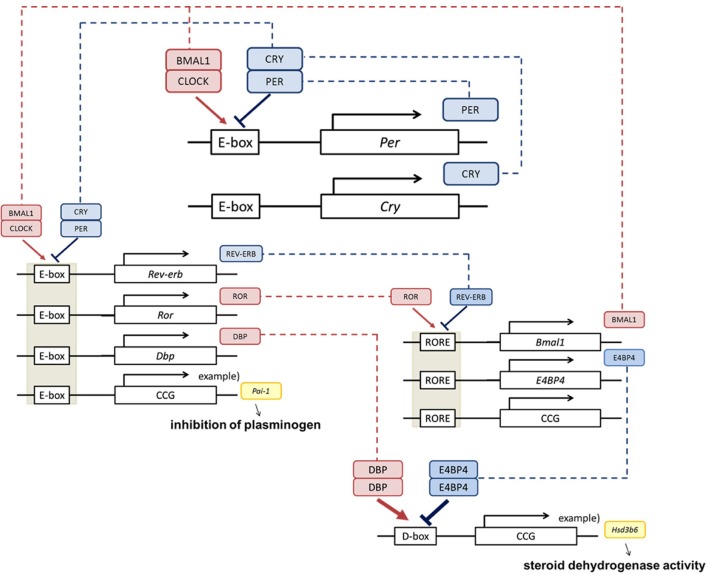
Figure 2.
Clock genes and physiological function. The core clock is composed by the Per, Cry, Bmal1, and Clock clock genes (Okamura et al., 2010; Takeda and Maemura, 2011). BMAL1 and CLOCK activate transcriptional levels through E-boxes, and CRY and PER suppress this activity. Cis elements such as RORE and D-box can be regulated by ROR, REV-ERB, DBP, and E4BP4, and multilayered rigid circadian rhythms are ticked down. This negative feedback loop produces the rhythm of transcription. These regulations are transmitted via transcriptional fluctuations of clock controlled genes (ccg) such as plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (Pai-1) (Maemura et al., 2000; Haus, 2007), type VI 3 beta-hydroxyl-steroid dehydrogenase (Hsd3b6) (Bass, 2012).