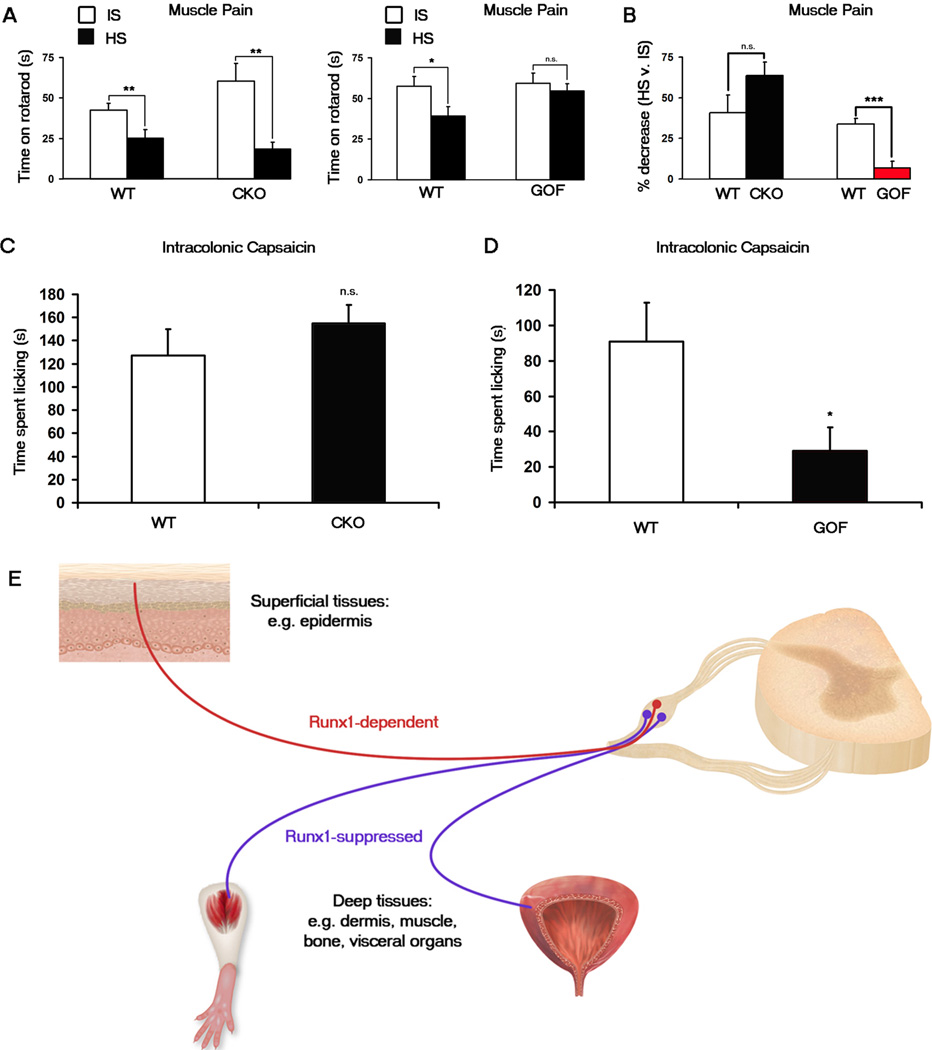
Figure 4. Muscle and visceral pain are impaired in Runx1 GOF mice but not in Runx1 CKO mice.
(A, B) Muscle pain assay. Time spent on an accelerating rotarod after the injection of hypertonic saline (“HS”) was compared with that after the injection of isotonic saline (“IS”). (A) Runx1 CKO (Runx1F/F;Wnt1Cre) mice (n = 9) displayed a significant decrease in rotatod performance after HS injection as did their WT (Runx1F/F) littermates (n = 9). Runx1 GOF (Nav1.8Cre;TauLSL-Runx1/+) mice (n = 8) displayed no significant decrease after HS injection in contrast to a significant decrease by their WT (TauLSL-Runx1/+) littermates (n = 8). (B) The percentage decrease after HS was calculated for each animal. Shown are the comparisons of the percentage decrease for the CKO and the GOF with their wild-type littermates. Error bars, SEM; * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; n.s., p ≥ 0.05.
(C, D) Intracolonic capsaicin injection visceral pain assay. (C) No difference in time spent licking between Runx1 CKO (Runx1F/F;Wnt1Cre) mice (n = 7) compared to their WT (Runx1F/F) littermates (n = 6). (D) Runx1 GOF (Nav1.8Cre;TauLSL-Runx1/+) mice (n = 7) displayed a significant decrease in time spent licking compared to their WT (TauLSLRunx1/+) littermates (n = 7). Error bars, SEM; * p < 0.05; n.s., p ≥ 0.05.
(E) Dynamic Runx1 expression and activity control the segregation of DRG neurons innervating the superficial ectodermal versus deep mesodermal/endodermal tissues. Neurons expressing Runx1-dependent genes innervate the skin epidermis and hair follicles, tissues fully or partly derived from the ectoderm; these neurons are required to sense cutaneous pain. Neurons expressing Runx1-suppressed genes innervate the mesodermal/endodermal tissues; these neurons are required to sense deep tissue pain. See also Figure S4.