Abstract
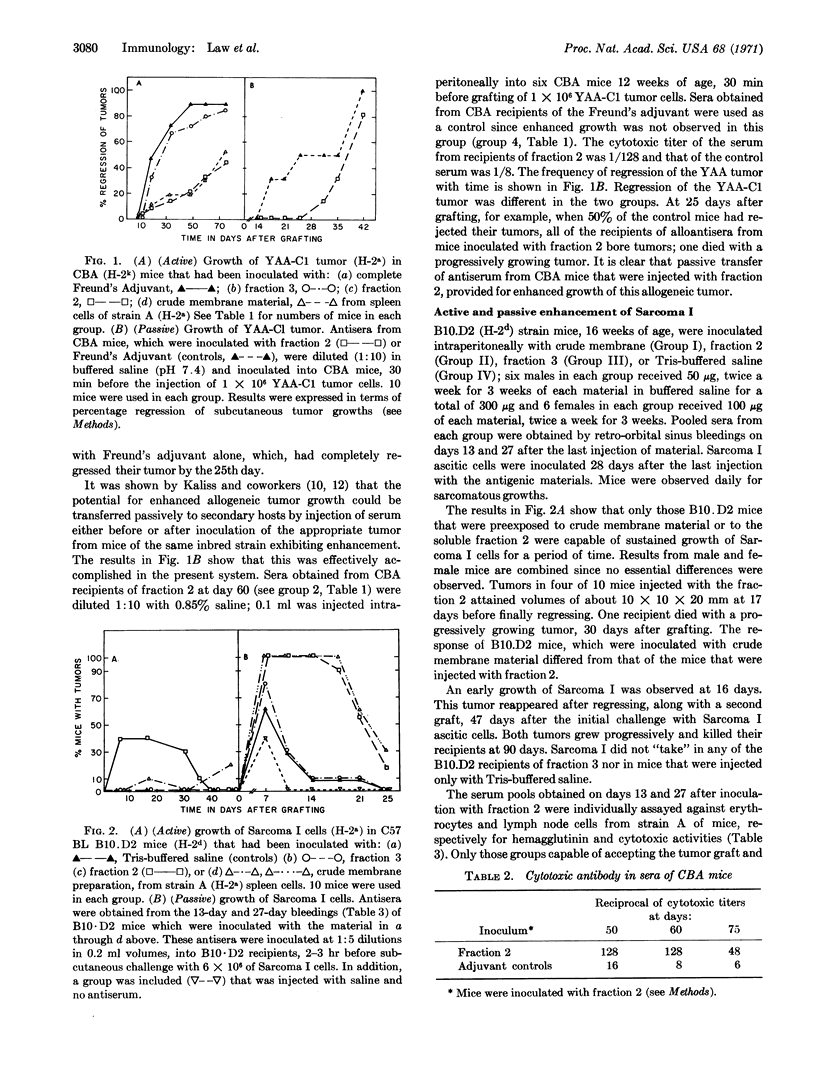
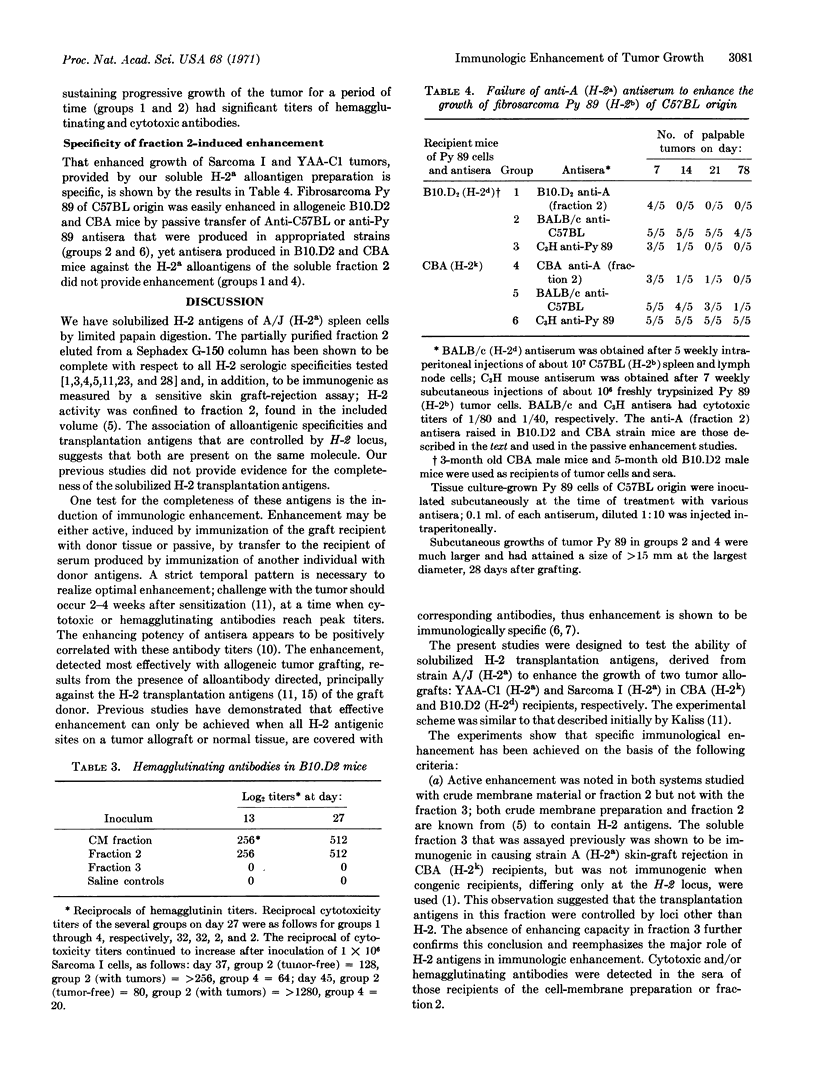
Soluble, partially purified, histocompatibility antigens that were obtained from the membranes of A/J spleen cells have been assayed for their capacity to elicit immunologic enhancement of two tumors of A-strain origin: YAA-C1 and Sarcoma I. Crude membrane material and a partially purified, soluble antigen that were contained in a specific fraction, obtained after chromatography on a Sephadex G-150 column, elicited enhancement; this fraction has been shown to contain immunogenic histocompatibility-2a antigens as well as alloantigenic specificities that were detected serologically. Another soluble fraction did not induce enhancement; this fraction has been shown to contain antigens other than H-2.
Passive enhancement of both tumors was achieved with antisera produced in allogeneic mice that were inoculated with crude membrane material or with a fraction obtained by Sephadex G-150 chromatography. These antisera contained cytotoxic and/or hemagglutinating antibodies. Immunologic enhancement was specific. A readily enhanceable tumor, Py 89, of C57BL origin was not enhanced with anti-H-2a antisera.
These results suggest strongly that all important H-2a transplantation antigenic determinants of spleen cells can be recovered by partial papain digestion and fractionation on a Sephadex G-150 column.
Keywords: tumor-specific transplantation antigen, mice, solubilization, immune tolerance
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Graff R. J., Mann D. L., Nathenson S. G. Immunogenic properties of papain-solubilized H-2 alloantigens. Transplantation. 1970 Jul;10(1):59–65. doi: 10.1097/00007890-197007000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graff R. J., Nathenson S. G. Immunogenic properties of papain-solubilized alloantigen. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):249–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Sjögren H. O. Demonstration of H-2 isoantigens and polyoma specific tumor antigens by measuring colony formation in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Oct;40(1):212–215. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALISS N. Acceptance of tumor homografts by mice injected with antiserum. II. Effect of time of injection. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Mar;91(3):432–437. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALISS N., KANDUTSCH A. A. Acceptance of tumor homografts by mice injected with antiserum. I. Activity of serum fractions. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jan;91(1):118–121. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaliss N. Immunological enhancement. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1969;8:241–276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER G. Studies on the mechanism of immunological enhancement of tumor homografts. I. Specificity of immunological enhancement. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Jun;30:1153–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada A., Nathenson S. G. Murine histocompatibility-2 (H-2) alloantigens. Purification and some chemical properties of soluble products from H-2b and H-2d genotypes released by papain digestion of membrane fractions. Biochemistry. 1969 Oct;8(10):4048–4062. doi: 10.1021/bi00838a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snell G. D. Immunologic enhancement. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1970 Jun;130(6):1109–1119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strober S., Appella E., Law L. W. Serological and immunogenic activity of soluble mouse transplantation antigens controlled by the H-2 locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Oct;67(2):765–772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TING R. C., LAW L. W. THE ROLE OF THYMUS IN TRANSPLANTATION RESISTANCE INDUCED BY POLYOMA VIRUS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1965 Apr;34:521–527. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Nathenson S. G. Biochemical similarity of papain-solubilized H-2d alloantigens from tumor cells and from normal cells. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4743–4750. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamane K., Nathenson S. G. Murine histocompatibility-2 (H-2) alloantigens. Purification and some chemical properties of a second class of fragments (class II) solubilized by papain from cell membranes of H-2b and H-2d mice. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1336–1341. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


