Figure 1.
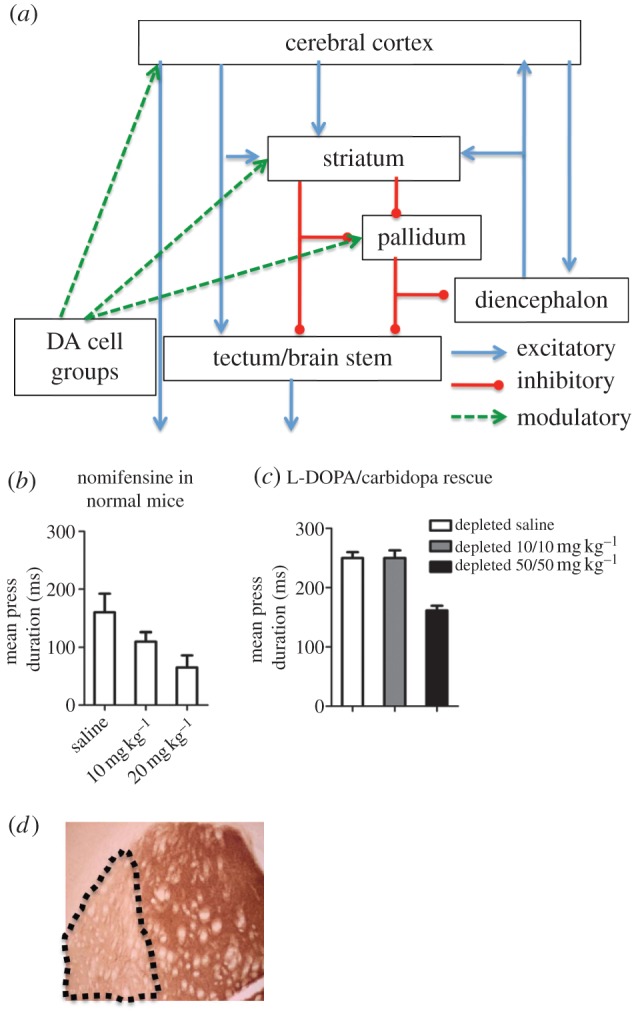
DA and action timing. (a) Schematic of the basic cortico-basal ganglia circuit. Cortical projection neurons, the pyramidal cells in layer 5, are glutamatergic and excitatory. Striatal and pallidal projection neurons are by contrast GABAergic and usually inhibitory. The modulatory dopaminergic projections target most components of the cortico-basal ganglia network, but by far the largest proportion target the striatum. (b) Intraperitoneal injection of nomifensine, a blocker of DA transporter, dose-dependently reduced duration of lever presses in normal mice (n = 5, p < 0.05). All mice were food deprived and maintained at approximately 85% of normal body weight. They were trained on a continuous reinforcement schedule for 4 days (each lever press earned a food pellet). They were then trained on a FI-60 schedule for at least 5 days before testing (1 h daily sessions). (c) DA depletion in the sensorimotor striatum increased the duration of lever presses, but this increase in press duration can be rescued with intraperitoneal injections of L-DOPA/carbidopa (n = 5, p < 0.0001). (d) A coronal section of the mouse brain with tyrosine hydroxylase staining showing selective depletion of DA in the lateral sensorimotor striatum after local 6-OHDA injections (20 mg ml−1, 0.5 µl per side to target dopaminergic terminals bilaterally in the striatum). Note that the lesion is selective, showing depletion limited to the sensorimotor striatum. Stereotaxic coordinates relative to bregma in mm: +0.5, ML ± 3.0 and −3 in dorsolateral striatum).
