Figure 2.
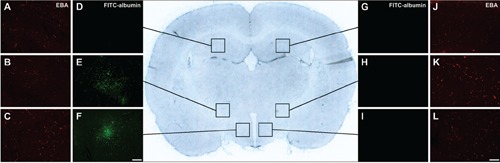
Representative overview scan from a coronal rat brain section 25 h after embolic stroke (center). Lateral inserts indicate cerebral vessels immunolabeled with anti-endothelial barrier antigen (EBA) on the ischemia-affected hemisphere (A,B,C) and the non-affected hemisphere (J,K,L), while fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-albumin, enhanced by carbocyanine (Cy)2-anti-FITC-IgG, indicated increased vascular permeability in terms of leakage (D, E and F on the ischemic vs G, H and I on the contralateral hemisphere). Generally, different parameters of EBA-immunolabeled structures in the striatum (middle inserts) as primarily affected area in the applied model of focal cerebral ischemia, as well as the hypothalamus (lower inserts), which was also involved in several cases, while the hippocampus (upper insets) with apparently intact blood-brain barrier served as control. Scale bars: A-L, 100 μm.
