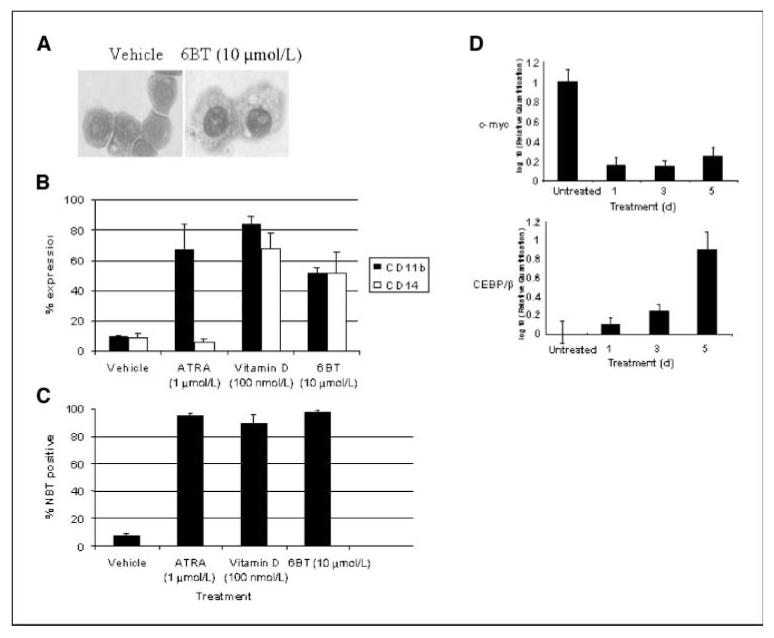
Figure 2.
6BT induces monocyte/macophage differentiation of HL-60 cells. A, 6BT induces morphologic changes consistent with monocyte/macrophage differentiation. After treatment for 4 d with 6BT, cytospin preparations were prepared and the cells were stained with wright-giemsa stain. Magnification, ×40. B, 6BT induces immunophenotypic changes consistent with monocytic differentiation. After treatment for 4 d, HL-60 cells were stained with CD11b-PE and CD14-FITC, and flow cytometric analysis was performed. Results are an average of three independent experiments. C, 6BT induces NBT reduction activity consistent with myelomonocytic differentiation. HL-60 cells were treated with the indicated compounds for 4 d and then the NBT reduction assay was performed. The percentage of NBT-positive cells was calculated by counting at least 200 cells under a light microscope. Results are an average of three independent experiments. D, 6BT induces the monocytic transcription factor CEBP/β and down-regulates the transcription factor c-myc. HL-60 cells were treated for the indicated number of days with vehicle or 10 μmol/L 6BT. The relative expression of CEBP/β and c-myc was determined by real-time PCR.