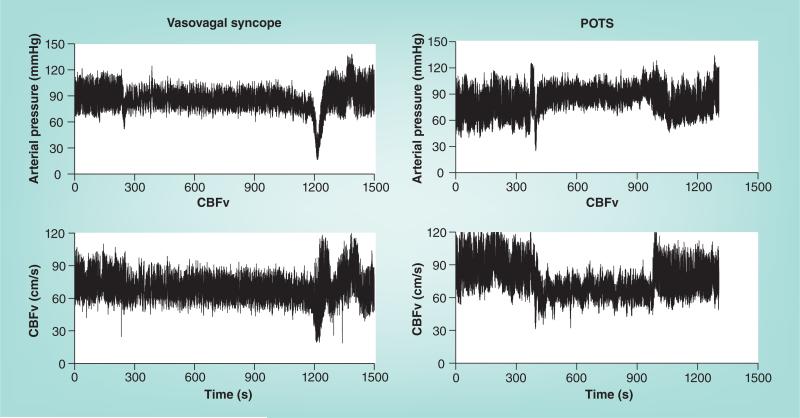
Figure 1. Arterial pressure (upper panels) and cerebral blood flow velocity measured by transcranial Doppler ultrasound (lower panels).
The left panels show data from a vasovagal syncope patient, while the right panels show data from a POTS patient. Arterial pressure and CBFv are initially stable, then decrease gradually and finally abruptly decrease by >50% with loss of consciousness in the syncope patient. The POTS patient has no decrease in arterial pressure, but has a >20% reduction in CBF throughout tilt.
CBFv: Cerebral blood flow velocity; POTS: Postural tachycardia syndrome.