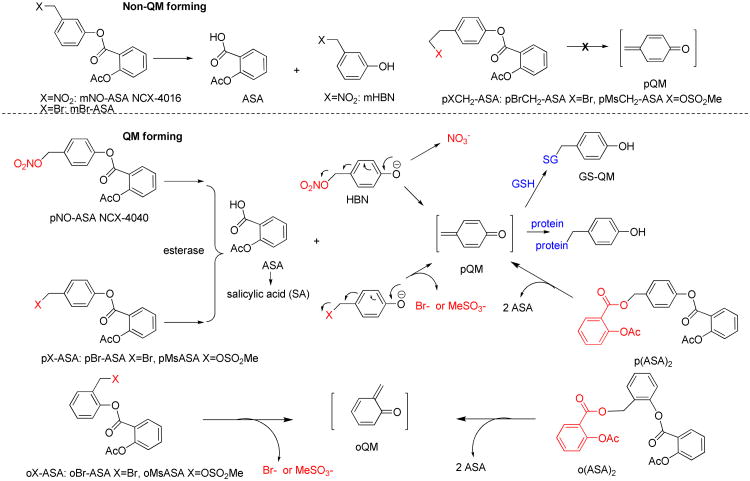
Figure 1.
Chemical structures of NO-ASA isomers, NCX-4016 (mNO-ASA) and NCX-4040 (pNO-ASA), and novel X-ASA and (ASA)2 derivatives. Esterase-mediated bioactivation liberates SA, ASA, and HBN. The quinone methide is formed from o- and p- isomers, but not from m-isomers. The highly reactive electrophilic QM depletes GSH and modifies Cys residues of proteins including GST-P1 and Keap1.